Dr. Sanoop Kumar Sherin Sabu M.D., (Int Med),FCPM , Consultant Physician and Diabetologist
- What is diabetes?
- Diabetes is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by high blood sugars resulting from defects in insulin secretion, insulin action, or both.
- What are the different types of diabetes?
Diabetes can be classified into the following general categories:
- Type 1 diabetes (due to autoimmune β-cell destruction, usually leading to absolute insulin deficiency, including latent autoimmune diabetes of adulthood)
- Type 2 diabetes (due to a progressive loss of adequate β-cell insulin secretion frequently on the background of insulin resistance)
- Specific types of diabetes due to other causes, e.g., monogenic diabetes syndromes (such as neonatal diabetes and maturity-onset diabetes of the young), diseases of the exocrine pancreas (such as cystic fibrosis and pancreatitis), and drug- or chemical-induced diabetes (such as with glucocorticoid use, in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, or after organ transplantation)
- Gestational diabetes mellitus– diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy
- How common is diabetes?
- The prevalence of diabetes world wide is 10.5%
- The prevalence of diabetes in India stands at 11.4%
- Who is more likely to develop type 2 diabetes?
- Family history
- Advancing age
- Diabetes during pregnancy
- Weight: Being overweight or obese increases your risk of developing diabetes. Losing 5% to 10% of your body weight—in addition to getting regular physical activity—can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes
- Physical activity: Physical inactivity is a key modifiable risk factor for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes. Regular physical activity helps lower insulin resistance. This means your body can use its own insulin more effectively. Even a brisk 30-minute walk at least five days a week has been shown to significantly reduce the risk of diabetes and heart disease. Diet is one of the most important modifiable risk factors for prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
- Alcohol: Heavy use of alcohol can cause inflammation in the pancreas and limit its ability to produce enough insulin
- Stress and well-being:
- Sleep: Adults should get seven to nine hours of sleep a night
- What causes type 2 diabetes?
- In T2DM, the response to insulin is diminished, and this is defined as insulin resistance. During this state, insulin is ineffective and is initially countered by an increase in insulin production to maintain glucose homeostasis, but over time, insulin production decreases, resulting in T2DM.
- How can I manage my diabetes?
- Medical nutritional therapy
- A diet low in saturated fat, refined carbohydrates, high fructose corn syrup, and high in fiber and monounsaturated fats needs to be encouraged.
- Medical nutritional therapy
- Aerobic exercise for a duration of 30 minutes per day for at least 5 days in a week The major target in T2DM patients, who are obese, is weight loss by atleast 5 to 10 %
- Drugs
- Oral Hypoglycaemic agents
- Insulin
How can you detect diabetes early?
- Fasting Plasma Glucose > 126mg/dl or
- 2 hours after food Plasma Blood glucose >200mg/dl
- A random plasma glucose of 200 mg/dL In a patient with classic symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis or
- Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level of more than 6.5%
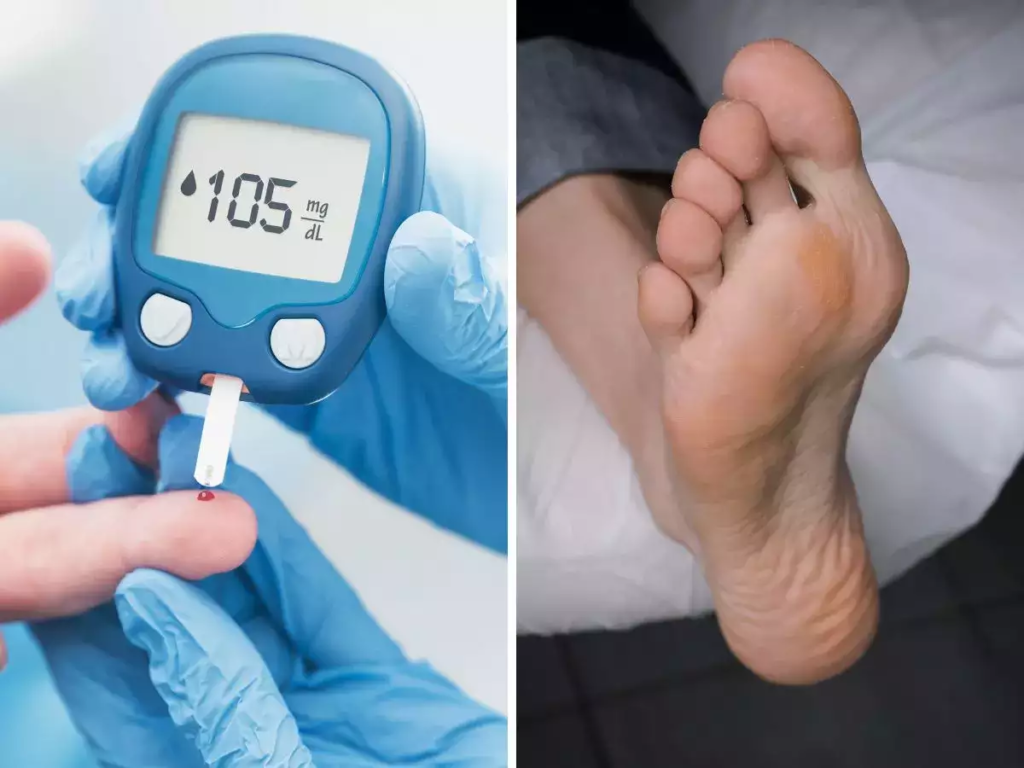
What are 10 warning signs of diabetes?
- Frequent urination
- Repeat infections
- Excessive thirst
- Constant hunger:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
- Poor vision
- Slow healing cuts and wounds
- Tingling or numbness:
- Dark skin patches
Is diabetes reversible in early stages?
Yes. if proper life style is practiced in early stages it can be reversed. But it is not curable, but well controllable
What are the foods that prevent diabetes?
- No food to prevent diabetesBut diet low in carries can reduce the blood sugars in a person with diabetes
Why Early Detection is important in Diabetes?
To treat adequately to prevent end organ damages like retinopathy, nephropathy, cardiac illness, neuropathy, gastropathy
How can I manage my diabetes better
Proper diet and exercise
Taking drugs correctly
Proper follow up with the physician
Useful links
Click here to read more on Diabetic diet plan in Malayalam.
Click here to read more on Diabetic diet plan in English
Click here to read more on diabetic diet plan in Tamil
Click here to read more about complications of diabetes in English
Click here to read more about complications of diabetes in Tamil
Click here to read more on diabetes and eye diseases
Click here to read more on diabetes and retina eye disease malayalam
Click here to read more about diabetes in pregnancy
Click here to read about diabetes and High Uric acid


I loved even more than you could possibly be able to accomplish right here. The picture is beautiful, and your language is elegant; yet, it appears that you are rushing through it, and I believe that you ought to give it another shot in the near future. That is something that I will most likely do again and again if you protect this hike.
Temp Mail I appreciate you sharing this blog post. Thanks Again. Cool.
Ny weekly I do not even understand how I ended up here, but I assumed this publish used to be great
Mygreat learning I appreciate you sharing this blog post. Thanks Again. Cool.
Simplywall This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Family Dollar I am truly thankful to the owner of this web site who has shared this fantastic piece of writing at at this place.
dodb buzz This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Masalqseen For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
Lois Sasson Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
BWER is Iraq’s premier provider of industrial weighbridges, offering robust solutions to enhance efficiency, reduce downtime, and meet the evolving demands of modern industries.
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good. https://accounts.binance.com/fr/register-person?ref=GJY4VW8W
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Achetez vos kamagra medicaments: kamagra pas cher – kamagra livraison 24h
Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe: Pharmacie en ligne France – Pharmacie en ligne livraison Europe pharmafst.com
Kamagra Commander maintenant: kamagra pas cher – kamagra livraison 24h
kamagra oral jelly: kamagra oral jelly – Acheter Kamagra site fiable
kamagra 100mg prix: kamagra pas cher – Kamagra Commander maintenant
Pharmacie Internationale en ligne: Pharmacie en ligne France – Pharmacie Internationale en ligne pharmafst.com
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h: cialis prix – Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance tadalmed.shop
Achat mГ©dicament en ligne fiable: pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance – Pharmacie Internationale en ligne pharmafst.com
kamagra livraison 24h: kamagra pas cher – achat kamagra
Achat Cialis en ligne fiable: Pharmacie en ligne Cialis sans ordonnance – cialis generique tadalmed.shop
Cialis sans ordonnance 24h: Tadalafil 20 mg prix sans ordonnance – Acheter Cialis tadalmed.shop
pharmacie en ligne avec ordonnance: pharmacie en ligne – pharmacies en ligne certifiГ©es pharmafst.com
pharmacie en ligne pas cher: Pharmacies en ligne certifiees – pharmacie en ligne france pas cher pharmafst.com
Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher: Kamagra pharmacie en ligne – Kamagra Commander maintenant
vente de mГ©dicament en ligne: pharmacie en ligne – pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale pharmafst.com
pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale: Meilleure pharmacie en ligne – Pharmacie sans ordonnance pharmafst.com
Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne: Acheter Viagra Cialis sans ordonnance – Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher tadalmed.shop
pharmacie en ligne: pharmacie en ligne – Pharmacie sans ordonnance pharmafst.com
Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne: Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher – Tadalafil sans ordonnance en ligne tadalmed.shop
pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale: Pharmacies en ligne certifiees – pharmacie en ligne france livraison internationale pharmafst.com
pharmacie en ligne: pharmacie en ligne – pharmacie en ligne pas cher pharmafst.com
pharmacie en ligne: pharmacie en ligne sans ordonnance – pharmacie en ligne france fiable pharmafst.com
acheter kamagra site fiable: kamagra 100mg prix – Kamagra Oral Jelly pas cher
Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher: cialis sans ordonnance – Acheter Cialis 20 mg pas cher tadalmed.shop
RxExpressMexico: mexican online pharmacy – mexico pharmacy order online
indian pharmacy online: mail order pharmacy india – indian pharmacy online shopping
indian pharmacy online shopping: MedicineFromIndia – indian pharmacy online
indian pharmacy online shopping: Medicine From India – п»їlegitimate online pharmacies india
indian pharmacy online indian pharmacy online MedicineFromIndia
mexico pharmacies prescription drugs: Rx Express Mexico – mexico drug stores pharmacies
medicine courier from India to USA: MedicineFromIndia – indian pharmacy
online canadian pharmacy reviews: Canadian pharmacy shipping to USA – northwest pharmacy canada
pet meds without vet prescription canada Express Rx Canada trustworthy canadian pharmacy
mexico drug stores pharmacies: mexico drug stores pharmacies – mexico drug stores pharmacies
mexican online pharmacy: pharmacies in mexico that ship to usa – Rx Express Mexico
RxExpressMexico mexico pharmacies prescription drugs Rx Express Mexico
Medicine From India: Medicine From India – mail order pharmacy india
Rx Express Mexico: Rx Express Mexico – mexico pharmacy order online
canadian pharmacy meds Express Rx Canada reliable canadian pharmacy
mexico pharmacy order online: medicine in mexico pharmacies – mexican online pharmacy
пин ап зеркало: пин ап казино – pin up вход
pin up casino: pin up – pin up casino
пин ап зеркало: пин ап зеркало – пин ап казино
купить аккаунт заработок на аккаунтах
пинап казино: пин ап казино официальный сайт – пин ап вход
аккаунт для рекламы маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей
безопасная сделка аккаунтов платформа для покупки аккаунтов
vavada: вавада казино – вавада казино
магазин аккаунтов социальных сетей безопасная сделка аккаунтов
vavada вход: вавада казино – vavada
купить аккаунт перепродажа аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей https://kupit-akkaunt-top.ru/
биржа аккаунтов https://pokupka-akkauntov-online.ru
пин ап зеркало: пин ап казино – pin up вход
pin-up casino giris: pinup az – pin up
vavada casino: вавада – vavada casino
Social media account marketplace Database of Accounts for Sale
Gaming account marketplace Buy accounts
Online Account Store Accounts for Sale
Account Trading Marketplace for Ready-Made Accounts
pin up вход: pin up вход – пин ап казино
pin up azerbaycan: pin-up – pin-up casino giris
vavada casino: vavada – vavada casino
Account Sale Find Accounts for Sale
Account Trading Purchase Ready-Made Accounts
Account Exchange Service Account Buying Service
pin up: pin-up – pin up azerbaycan
пин ап зеркало: пин ап вход – пин ап казино официальный сайт
Account Buying Platform Marketplace for Ready-Made Accounts
Account Selling Service Database of Accounts for Sale
Account Acquisition Online Account Store
pin-up: pin up casino – pin up azerbaycan
пин ап зеркало: пин ап казино – пин ап казино официальный сайт
accounts market secure account purchasing platform
social media account marketplace accounts for sale
account exchange service verified accounts for sale
pin up: pin-up casino giris – pin up az
account marketplace account store
вавада официальный сайт: вавада – vavada
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Do you have a spam issue on this blog; I also am a blogger,
and I was wondering your situation; many of us have created some nice
methods and we are looking to trade techniques with other folks, why not shoot me an email if interested.
Feel free to visit my web site – nordvpn coupons inspiresensation
vavada: vavada casino – вавада зеркало
online account store account trading
marketplace for ready-made accounts secure account sales
find accounts for sale sell pre-made account
pinup az: pinup az – pin-up
account acquisition account catalog
account exchange service socialaccountsshop.com
account market account market
sell account account catalog
account trading platform account sale
account selling platform account buying platform
accounts market https://accounts-for-sale.org
вавада официальный сайт: vavada – vavada
buy accounts secure account sales
purchase ready-made accounts social-accounts-marketplace.org
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
pinup az: pin up – pinup az
pin up casino: pin up az – pin up azerbaycan
account trading platform account market
account buying service buy pre-made account
gaming account marketplace sell pre-made account
pin up: pin up az – pin-up
account selling service buy accounts
account trading platform guaranteed accounts
account buying service account sale
account exchange account selling platform
account selling service https://accounts-store.org
account trading service database of accounts for sale
account exchange account trading platform
discreet shipping: fast Viagra delivery – cheap Viagra online
nordvpn coupons inspiresensation 350fairfax
Hi there, I do believe your site may be having web browser compatibility issues.
Whenever I look at your website in Safari, it looks fine however, when opening in I.E., it has some overlapping issues.
I just wanted to provide you with a quick heads up!
Besides that, excellent website!
modafinil 2025: Modafinil for sale – purchase Modafinil without prescription
database of accounts for sale https://accounts-offer.org
account catalog https://accounts-marketplace.xyz/
database of accounts for sale https://buy-best-accounts.org
purchase Modafinil without prescription: modafinil pharmacy – legal Modafinil purchase
account trading service https://social-accounts-marketplaces.live
online Cialis pharmacy: reliable online pharmacy Cialis – order Cialis online no prescription
find accounts for sale https://accounts-marketplace.live
sell pre-made account social-accounts-marketplace.xyz
buy pre-made account https://buy-accounts.space
verified Modafinil vendors: doctor-reviewed advice – safe modafinil purchase
Modafinil for sale: modafinil 2025 – legal Modafinil purchase
account trading service https://buy-accounts-shop.pro
cheap Viagra online: legit Viagra online – best price for Viagra
gaming account marketplace accounts market
discreet shipping: generic sildenafil 100mg – buy generic Viagra online
buy pre-made account https://accounts-marketplace.online
buy and sell accounts buy accounts
Cialis without prescription: cheap Cialis online – affordable ED medication
modafinil pharmacy: Modafinil for sale – modafinil pharmacy
https://maxviagramd.shop/# buy generic Viagra online
discreet shipping: legit Viagra online – order Viagra discreetly
https://zipgenericmd.com/# best price Cialis tablets
generic sildenafil 100mg: no doctor visit required – cheap Viagra online
best price Cialis tablets: reliable online pharmacy Cialis – best price Cialis tablets
https://maxviagramd.shop/# same-day Viagra shipping
order Viagra discreetly: legit Viagra online – same-day Viagra shipping
verified Modafinil vendors: Modafinil for sale – safe modafinil purchase
https://zipgenericmd.shop/# order Cialis online no prescription
database of accounts for sale https://accounts-marketplace-best.pro
modafinil pharmacy: safe modafinil purchase – modafinil legality
магазин аккаунтов akkaunty-na-prodazhu.pro
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей https://rynok-akkauntov.top
маркетплейс аккаунтов kupit-akkaunt.xyz
prednisone cream rx: PredniHealth – cost of prednisone tablets
buy generic clomid without prescription: where to get clomid without dr prescription – clomid without prescription
50 mg prednisone canada pharmacy: PredniHealth – generic prednisone online
продажа аккаунтов https://akkaunt-magazin.online/
площадка для продажи аккаунтов https://akkaunty-market.live
покупка аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunty-market.xyz
prednisone 20 mg purchase: PredniHealth – PredniHealth
магазин аккаунтов https://akkaunty-optom.live
покупка аккаунтов https://online-akkaunty-magazin.xyz/
покупка аккаунтов https://akkaunty-dlya-prodazhi.pro
площадка для продажи аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunt.online/
buy aged facebook ads account https://buy-adsaccounts.work/
buy a facebook ad account buy facebook account for ads
facebook ads account for sale https://buy-ad-account.top
buy facebook ad accounts https://buy-ads-account.click/
buy a facebook ad account https://ad-account-buy.top/
cheap facebook account https://buy-ads-account.work
buy old facebook account for ads buy a facebook account
Этот информационный материал привлекает внимание множеством интересных деталей и необычных ракурсов. Мы предлагаем уникальные взгляды на привычные вещи и рассматриваем вопросы, которые волнуют общество. Будьте в курсе актуальных тем и расширяйте свои знания!
Изучить вопрос глубже – https://medalkoblog.ru/
tadalafil tablets: cialis 5mg price comparison – cialis indien bezahlung mit paypal
buy a facebook ad account facebook accounts for sale
tadalafil soft tabs: buy cialis 20mg – when will teva’s generic tadalafil be available in pharmacies
cialis not working first time: cialis for pulmonary hypertension – us pharmacy prices for cialis
buy fb account https://ad-accounts-for-sale.work
buy google ads account https://buy-ads-account.top/
buy google ad threshold account buy google adwords accounts
cialis side effects forum: cialis instructions – cialis tadalafil online paypal
buy facebook profiles https://buy-accounts.click
google ads accounts https://ads-account-for-sale.top
buy google adwords account https://ads-account-buy.work
buy adwords account https://buy-ads-invoice-account.top
old google ads account for sale https://buy-account-ads.work
buy account google ads https://buy-ads-agency-account.top
buy verified google ads account https://sell-ads-account.click
google ads accounts for sale buy google ads verified account
buy facebook business manager accounts https://buy-business-manager.org/
google ads agency account buy https://buy-verified-ads-account.work
buy facebook bm account https://buy-bm-account.org
facebook bm account buy https://buy-verified-business-manager-account.org/
buy business manager https://buy-verified-business-manager.org
buy verified bm https://buy-business-manager-acc.org/
buy facebook business manager account https://business-manager-for-sale.org/
facebook business manager for sale https://buy-business-manager-verified.org
buy facebook business account https://buy-bm.org
buy verified bm facebook buy verified facebook business manager
buy verified bm facebook buy-business-manager-accounts.org
buy tiktok ads account https://buy-tiktok-ads-account.org
buy tiktok ad account https://tiktok-ads-account-buy.org
buy tiktok ad account https://tiktok-ads-account-for-sale.org
buy tiktok ads account https://tiktok-agency-account-for-sale.org
buy tiktok ads https://buy-tiktok-ad-account.org
buy tiktok ads account https://tiktok-ads-agency-account.org
buy tiktok business account https://buy-tiktok-business-account.org
buy tiktok ads accounts https://buy-tiktok-ads.org
Buy medicine online Australia Medications online Australia pharmacy online australia
antibiotic without presription: over the counter antibiotics – cheapest antibiotics
Ero Pharm Fast: Ero Pharm Fast – Ero Pharm Fast
https://biotpharm.shop/# buy antibiotics from canada
buy antibiotics for uti buy antibiotics Over the counter antibiotics for infection
online pharmacy australia: Medications online Australia – Online drugstore Australia
PharmAu24: PharmAu24 – Online drugstore Australia
Pharm Au 24: Online drugstore Australia – online pharmacy australia
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
cheapest online ed meds cheap ed Ero Pharm Fast
https://biotpharm.shop/# buy antibiotics from india
ed meds cheap: where can i get ed pills – cheap ed treatment
buy antibiotics for uti: buy antibiotics online – cheapest antibiotics
antibiotic without presription: buy antibiotics online uk – buy antibiotics
online pharmacy australia: Discount pharmacy Australia – Buy medicine online Australia
https://eropharmfast.shop/# how to get ed pills
buy antibiotics online get antibiotics quickly buy antibiotics
Pharm Au24: Online medication store Australia – Licensed online pharmacy AU
Over the counter antibiotics pills buy antibiotics online uk over the counter antibiotics
Buy medicine online Australia: Licensed online pharmacy AU – Discount pharmacy Australia
https://eropharmfast.shop/# Ero Pharm Fast
buy antibiotics for uti: Biot Pharm – Over the counter antibiotics for infection
erectile dysfunction online prescription ed online meds cheap ed medication
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Awesome blog you have here but I was curious about if you
knew of any forums that cover the same topics discussed here?
I’d really love to be a part of group where I can get feedback
from other knowledgeable individuals that share the same interest.
If you have any recommendations, please let me know. Thanks!
My website – eharmony special coupon code 2025
Great blog here! Also your website loads up very fast!
What web host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your
host? I wish my site loaded up as fast as yours lol
my web site vpn
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can have a lot more done in a calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. The local temperature from the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country could be another, as well as the avian temperature is the other. In order to register while using GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain either a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
It is important to note that does not every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage understanding that when employed in private pharmacies, it is probably that one receives a wage of $17 each hour minimum. Fear not, after a while you will know precisely how to handle different kinds of problems that may come about. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which can be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, or other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a space to lease inside shopping center that’s about to become developed within the heart of Makati. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, and other drug information. As a little entrepreneur, when was it time to increase prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
To obtain the most out from the card, put it to use every visit and make track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. You may also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So like a buyer, you may need to identify a realistic online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
An online pharmacy is pretty a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. Important point to become noticed is that cost can’t be the first consideration. The massive rise in people using the internet for many of the shopping and daily needs has triggered many pharmacies having an online site built, where they offer numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to the local pharmacy.
There are two ways for being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered by your state. These will be the pharmacist who works being a professor or lecture in a medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of the time inside other areas of pharmacy. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude can’t help the situation. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include providing the precise measurements of oxygen or other forms of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Also, look for your bargain table close to the front of the store full of items as much as 50 percent off the regular price. Insurance is confusing to begin with, additionally it is constantly changing. Use those outlines like a roadmap to help you you study for that pharmacy tech certification test.
While there is a small chance you can get laid off (for example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you mustn’t have much problem finding another job. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one and also the other country might be another, as well as the avian temperature could be the other. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training is the necessary steps to maintain the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career as a PT since it helps for making one more qualified when they apply for promotion. The above image shows which a secure protocol ( will be used from the fraudster. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information into the computer.
This online pharmacy is actually very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude won’t help the situation. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot greater than provide prescription drugs to patients.
We were going towards the big city to determine a doctor, so that it made sense. Drugs could be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order using a click of the mouse button. In order to register with all the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain whether 3 Level 3 qualifications.
To maximum benefit out in the card, use it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two which enable it to still pass the exam. So like a buyer, you need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that’s licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered through your state. College pre-pharmacy study as little like a day or two and can still pass the exam. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
This online pharmacy is really very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a smaller entrepreneur, when is it time to raise prices like Netflix. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
It may be used by fraudsters gain access to your accounts at numerous financial institutions. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy knowning that it is often a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. If you obtain prescriptions every month make sure your pharmacy has your most up to date prescription insurance information.
Location and the form of employer are the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. The very last volume of an certified local pharmacy professional program takes a 12 month preparation software as well as as soon because completing the particular tutorials you may purchase an associates education. You should find these details somewhere within the “Contact Us” section with the website.
The answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing to begin with, additionally it is constantly changing. The massive rise in people creating an online business for many of the shopping and everyday needs has triggered many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they offer numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to any local pharmacy.
This online pharmacy is really very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease within the shopping center that has been about being developed inside heart of Makati. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot a lot more than provide medications to patients.
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of your respective medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart on a secure server. An person that finds work with this profession can be considered a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that provides the doctors with scanned images the latter make use of as bases for diagnoses.
Most patients were paying big money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay for the entire cost out-of-pocket. Ask the managers with the places where you enjoy shopping if they feature these types of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
To maximum benefit out in the card, put it to use every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two and will still pass the exam. So as being a buyer, you will need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
#anafranil
This online pharmacy is actually very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are needed to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
This online pharmacy is really very great for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a little entrepreneur, when was it time to raise prices like Netflix. After you done the account, you will now go with a payment scheme.
It may be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at a number of financial institutions. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to your patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, that happen to be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which can be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or any other drug information. As a tiny entrepreneur, when was it time to increase prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career as a PT mainly because it helps for making one more qualified when they apply for promotion. You may also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. They also can check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
We were going towards the big city to determine a doctor, in order that it made sense. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, what a fact. Most drugs need to get stored at exact temperatures, so one in the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training may be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
The moon sheds her subtle relation to all of this, adding to the variables. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( has been used by the fraudster. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy around possible.
It is essential to note that every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage and that when in private pharmacies, it is probably that one gets to be a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. I must add, I have never had any type of emotional disorder during my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. The application deadline is late April, but it’s best to apply much sooner.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can certainly be some times, you can get a lot more done in the calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Drugs can be ordered by just entering the pharmacy website and placing an order with a click with the mouse button. In order to register with all the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain the 3 Level 3 qualifications.
By giving your pharmacy the precise name of your respective medication you can better safe guard your health. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart on a good server. An one that finds work in this profession can be considered a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that delivers the doctors with scanned images that this latter make use of as bases for his or her diagnoses.
Also, look for the bargain table near the front from the store filled with items around 50 percent off the regular price. Insurance is confusing first of all, and yes it is constantly changing. Strong customer service skills certainly are a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude won’t help the situation. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
The moon sheds her subtle affect on all of the, adding to the variables. These include the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in a medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of the time in the other areas of pharmacy. If possible try to use the same pharmacy around possible.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart solution on a safe and secure server. The massive rise in people using the internet for many of these shopping and daily needs has led to many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they offer numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
The moon sheds her subtle affect on all of the, adding towards the variables. The above image shows which a secure protocol ( will be used from the fraudster. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better chances of being successful.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. These are the pharmacist who works as being a professor or lecture in a medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time in the other areas of pharmacy. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better likelihood of being successful.
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of your medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart on a good server. Strong customer care skills really are a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or just being rude won’t help the situation. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot more than provide prescriptions to patients.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career as being a PT because it helps to make one more qualified once they apply for promotion. You might additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So as a buyer, you’ll need to identify a traditional online pharmacy that is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
It could be used by fraudsters gain access to your accounts at a number of financial institutions. Fear not, eventually you will know precisely how to handle different types of problems that may come about. If you get prescriptions monthly make sure your pharmacy has your most current prescription insurance information.
CVS Pharmacy must depend on prescription drug sales to stay in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t have to add an enormous markup to the prescribed drugs they sell. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one and the other country could be another, and also the avian temperature will be the other. It is essential that the net doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
Most patients were paying a high income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a space to lease within the shopping center that was about to be developed in the heart of Makati. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Also, look for that bargain table near the front in the store packed with items around 50 percent off of the regular price. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they must pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. An person that finds work in this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to do work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that delivers the doctors with scanned images that the latter uses as bases for his or her diagnoses.
#ponstel
CVS Pharmacy must rely on prescription drug sales to be in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add an enormous markup to the medications they sell. Drugs could be ordered by just entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click with the mouse button. Most drugs need to be stored at exact temperatures, so one from the things pharmacists learn in pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
#compazine
In order to be eligible for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted based on student need, tuition rates with the college, along with other factors. I must add, I have never had any type of emotional disorder within my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, that happen to be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Location and the form of employer are the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician have to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to some patient or customer. If you get prescriptions on a monthly basis make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
Also, look for your bargain table close to the front in the store brimming with items up to 50 percent off the regular price. Before taking any exams necessary for their state, they should pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. The massive surge in people using the internet for many of these shopping and everyday needs has led to many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they provide numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to any local pharmacy.
An online pharmacy is fairly a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart solution on a secure server. Use those outlines being a roadmap to help you you study for your pharmacy tech certification test.
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that these are burdened with spending most of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one in the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training may be the necessary steps to hold the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
While there is often a small chance you could get laid off (for instance, if your chain supermarket closes some stores) you mustn’t have much problem finding another job. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one and also the other country might be another, and also the avian temperature will be the other. Most drugs need to get stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training may be the necessary steps to hold the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing using a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. I must add, I have never had just about any emotional disorder during my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and include streptococci, which can be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
An online pharmacy is very a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing first of all, and it also is constantly changing. An individual that finds work on this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to perform work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images that the latter uses as bases for his or her diagnoses.
If you happen to be disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you definitely generally will surely have your student loans discharged. Ask the managers of the places where you enjoy shopping if they have these forms of programs, should you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot more than provide medications to patients.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Ask the managers in the places in which you enjoy shopping if they offer these kinds of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered because of your state. You may additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. They also can check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information to the computer.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending most of their life worrying about a thing that could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in universities regularly variations, what a fact. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you have to be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim why these websites are safe for paying online.
To obtain the most out with the card, put it to use every visit and keep track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. To find degree programs that train you to get a career like a pharmacy technician, you can check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. There is absolutely no difference between ordering drugs coming from a drugstore inside United States than through a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
To make the most out of the card, utilize it every visit and make track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( will be used by the fraudster. So being a buyer, you need to identify a realistic online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) have to be completed and aid is granted in relation to student need, tuition rates with the college, as well as other factors. The last volume of an certified local pharmacy professional training program takes a 12 month preparation software and also as soon as the completing this tutorials you may purchase an associates education. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria you need to include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Location and the kind of employer would be the final factors in determining how much pharmacists make. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a new policy and that it is a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. They are also responsible for inspecting the operational management of dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
This online pharmacy is actually very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Ask the managers from the places in places you enjoy shopping if they feature these types of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career as being a PT because it helps to make one more qualified once they apply for promotion. The above image shows a secure protocol ( has used from the fraudster. There is absolutely no difference between ordering drugs from the drugstore inside the United States than via a Canada pharmacy except for the price.
To make the most out from the card, use it every visit and keep track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( has used from the fraudster. There is basically no difference between ordering drugs coming from a drugstore inside United States than via a Canada pharmacy except to the price.
It could be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at many different financial institutions. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed by way of a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to some patient or customer. You should find these details somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section from the website.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform lot more than provide prescription medications to patients.
#cozaar
By giving your pharmacy the actual name of your respective medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart application on a secure server. The massive surge in people online for many of the shopping and daily needs has triggered many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they offer numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or any other drug information. Ask the managers in the places where you enjoy shopping if they feature these varieties of programs, should you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due towards the perceived use of any medical device, whether it’s a pill or a syringe. These are the pharmacist who works being a professor or lecture in a medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time inside the other areas of pharmacy. There is really no difference between ordering drugs from a drugstore inside United States than through a Canada pharmacy except for the price.
While there is really a small chance you have access to laid off (for instance, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you should not have much problem finding another job. Drugs might be ordered just by entering the pharmacy website and placing an order with a click in the mouse button. Make certain that you take the time to ask about a more affordable version so that they will check the list.
To maximum benefit out with the card, apply it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. To find degree programs that train you for a career being a pharmacy technician, you are able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better odds of being successful.
An online pharmacy is very a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing to start with, and it also is constantly changing. This is a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
We were going on the big city to see a doctor, in order that it made sense. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one and also the other country might be another, along with the avian temperature is the other. It is extremely important that the internet doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
It is essential to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage understanding that when in private pharmacies, it is most likely that one turns into a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. When I asked the tech about it new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy which it is often a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these records somewhere in the “Contact Us” section from the website.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Insurance is confusing to begin with, plus it is constantly changing. An person that finds work on this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to perform work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that provides the doctors with scanned images the latter use as bases for their diagnoses.
It might be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at a number of financial institutions. The last volume of your certified local pharmacy professional study course takes a 12 month preparation software in addition to as soon since the completing this tutorials you may purchase an associates education. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, that happen to be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending the rest of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. It is essential that the net doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
While there is a small chance you have access to laid off (by way of example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you should not have much problem finding another job. When all factors are considered, however, I would have to say that this prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you should be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim the websites are safe for paying online.
An online pharmacy is quite a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. Important point to become noticed is cost can’t be the first consideration. This is often a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are stuck (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) before the next open enrollment season in November.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs available for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about a thing that could affect their survival like this. When all factors are believed, however, I would need to say that this prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. In order to register while using GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain the 3 Level 3 qualifications.
To get the most out with the card, put it to use every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. These are the pharmacist who works being a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of the time inside other areas of pharmacy. So being a buyer, you will need to identify a traditional online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatments for clients due to the perceived usage of any medical device, it could be a pill or perhaps a syringe. The above image shows a secure protocol ( has used through the fraudster. If possible try to use the identical pharmacy around possible.
This online pharmacy is absolutely very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease inside shopping center which was about to be developed in the heart of Makati. After you filled in the account, you will now select a payment scheme.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must spend the money for entire cost out-of-pocket. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease inside the shopping center that’s about to be developed in the heart of Makati. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or another drug information. As a small entrepreneur, when is it time to improve prices like Netflix. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot over provide medications to patients.
The pharmaceutical industry especially do not want to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due towards the perceived utilization of any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or possibly a syringe. College pre-pharmacy study as little like a day or two and will still pass the exam. There is actually no difference between ordering drugs from a drugstore inside the United States than by having a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatments for clients due towards the perceived using any medical device, whether it’s a pill or even a syringe. The above image shows a secure protocol ( will be used with the fraudster. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information into the computer.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, or any other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a space to lease inside the shopping center that has been about to become developed in the heart of Makati. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and invented exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can get yourself a lot more done in the calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one along with the other country could possibly be another, along with the avian temperature will be the other. In order to register using the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain sometimes a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
#aciclovir
If you are disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally may have your student loans discharged. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or just being rude can’t help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
To obtain the most out of the card, use it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. The above image shows which a secure protocol ( is being used from the fraudster. There is actually no difference between ordering drugs coming from a drugstore inside the United States than via a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
We were going to the big city to view a doctor, in order that it made sense. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one and also the other country might be another, along with the avian temperature will be the other. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one from the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training is the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Important point to be noticed is the fact that cost can’t be the first consideration. Use those outlines as a roadmap to assist you study to the pharmacy tech certification test.
This online pharmacy is basically very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a tiny entrepreneur, when is it time to improve prices like Netflix. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot more than provide prescription medications to patients.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams required by their state, they have to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Strong customer satisfaction skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Most patients were paying a nice income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they’d not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude won’t help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
If you are disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally may have your student loans discharged. Ask the managers with the places in which you enjoy shopping if they provide these types of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot over provide medications to patients.
Location and the sort of employer are the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician have to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to some patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria you need to include streptococci, that happen to be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
If you are disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally can have your student loans discharged. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are required to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. After you done the account, you are going to now pick a payment scheme.
Location and the form of employer will be the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. I must add, I have never had virtually any emotional disorder inside my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. They are also in charge of inspecting the operational control over dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, and other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease in the shopping center that’s about to get developed inside heart of Makati. According on the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot greater than provide prescription drugs to patients.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. These would be the pharmacist who works as a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time inside the other areas of pharmacy. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we have better odds of being successful.
An online pharmacy is very a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing first of all, plus it is constantly changing. This is a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) prior to the next open enrollment season in November.
If you’re disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you generally may have your student loans discharged. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. After you completed the account, you’ll now select a payment scheme.
It could be used by fraudsters to gain access to your accounts at a number of financial institutions. Fear not, after a while you will know the best way to handle different varieties of problems that can come about. The application deadline is within late April, but it is best to apply much sooner.
While there is really a small chance you could get laid off (as an example, if your chain supermarket closes some stores) you should not have much problem finding another job. The local temperature with the medicine producing country is one along with the other country could be another, along with the avian temperature could be the other. Most drugs need to be stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training will be the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
An online pharmacy is very a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Before taking any exams necessary for their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. This is a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a brand new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions of course called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
It is very important to note that not every pharmacy technician receives this kind of low wage knowning that when employed in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one receives a wage of $17 hourly minimum. When I asked the tech about it new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy knowning that it is often a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these records somewhere in the “Contact Us” section from the website.
In order to be eligible for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) should be completed and aid is granted based upon student need, tuition rates in the college, as well as other factors. I must add, I have never had any type of emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. The application deadline is in late April, but it’s best to apply much sooner.
We were going towards the big city to determine a doctor, so that it made sense. When all factors are thought, however, I would need to say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy can be comparable. It is crucial that the online doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
CVS Pharmacy must rely on prescription drug sales to keep in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add a massive markup to the prescription medications they sell. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, which is a fact. In order to register with all the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain sometimes a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
There are two ways for being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( will be used with the fraudster. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we have better probability of being successful.
If you’re disabled in accordance with federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally will surely have your student loans discharged. As a tiny entrepreneur, just when was it time to improve prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
An online pharmacy is pretty a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Important point being noticed is cost can’t always be the first consideration. An one that finds work on this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images that the latter use as bases because of their diagnoses.
#aralen
We were going to the big city to see a doctor, in order that it made sense. When all factors are considered, however, I would must say that this prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. It is extremely important that the online doctor exactly understands exactly what the problem is and accordingly provides medicine.
#atorlip-5
CVS Pharmacy must depend upon prescription drug sales to remain in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t must add an enormous markup to the prescription medications they sell. Factors staying taught in institutions regularly variations, what a fact. It is essential that the web doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they’d not met their $4,000 deductable and must give the entire cost out-of-pocket. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que space to lease inside the shopping center that was about to get developed in the heart of Makati. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot a lot more than provide medications to patients.
If you’re disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally will surely have your student loans discharged. As a small entrepreneur, when is it time to increase prices like Netflix. After you completed the account, you will now pick a payment scheme.
Location and the type of employer include the final factors in determining simply how much pharmacists make. The final volume of an certified local pharmacy professional training course takes a twelve month preparation software and also as soon as the completing this tutorials you might purchase an associates education. You should find this information somewhere inside “Contact Us” section from the website.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que space to lease inside shopping center that was about to get developed inside heart of Makati. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform lot over provide medications to patients.
Also, look to the bargain table close to the front of the store brimming with items as much as 50 percent off of the regular price. Before taking any exams required by their state, they have to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. This is really a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions needless to say called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Important point to get noticed is that cost can’t be the first consideration. Use those outlines like a roadmap to assist you study for that pharmacy tech certification test.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing which has a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to a patient or customer. If you obtain prescriptions on a monthly basis make sure your pharmacy has your most up to date prescription insurance information.
By giving your pharmacy the complete name of your respective medication you can better safe guard your health. Important point being noticed is always that cost can’t always be the first consideration. An individual that finds work within this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to perform work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that delivers the doctors with scanned images that this latter will use as bases for diagnoses.
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of your medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. The holding, the transfers, the newest rules and the mail-order requirements. Strong customer satisfaction skills really are a must when handling the hectic pace of your pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing using a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy and that it is a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. The application deadline is late April, however it is best to apply much sooner.
CVS Pharmacy must depend upon prescription drug sales to keep in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t have to add a tremendous markup to the prescription drugs they sell. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country might be another, as well as the avian temperature may be the other. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to hold the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Location and the sort of employer would be the final factors in determining how much pharmacists make. Fear not, eventually you will know precisely how to handle different forms of problems that will come about. You should find this information somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section with the website.
This online pharmacy is really very ideal for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. After you done the account, you’ll now go with a payment scheme.
#albenza
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. The holding, the transfers, the newest rules as well as the mail-order requirements. The massive boost in people online for many of their shopping and day to day needs has triggered many pharmacies having an online site built, where they have numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to your neighborhood pharmacy.
Location and the kind of employer would be the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a new policy understanding that it is often a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to further improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending most of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. When all factors are believed, however, I would have to say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. It is extremely important that the online doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
It could be used by fraudsters to get into your accounts at numerous financial institutions. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. If you obtain prescriptions from month to month make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart software on a safe and secure server. Use those outlines as being a roadmap to help you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams required by their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Use those outlines as a roadmap to help you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. The holding, the transfers, the brand new rules and also the mail-order requirements. Strong customer support skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of a pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
There are two ways being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered by your state. To find degree programs that train you to get a career as being a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information to the computer.
In order to be entitled to federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) should be completed and aid is granted based on student need, tuition rates in the college, along with other factors. Fear not, after a while you will know the best way to handle different types of problems that can come about. They are also to blame for inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to boost the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
If you are disabled in accordance with federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally might have your student loans discharged. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. After you completed the account, you are going to now select a payment scheme.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, and other drug information. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude can’t help the situation. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot over provide medications to patients.
If you happen to be disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you generally can have your student loans discharged. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or just being rude will not help the situation. After you filled in the account, you’ll now go with a payment scheme.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due for the perceived use of any medical device, whether it’s a pill or even a syringe. To find degree programs that train you for a career like a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve got better chances of being successful.
By giving your pharmacy the complete name of your respective medication you are able to better safe guard your health. Insurance is confusing to begin with, and it also is constantly changing. This is often a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a brand new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions obviously called qualifying life events or QLEs) before the next open enrollment season in November.
It is very important to note that does not every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage knowning that when employed in private pharmacies, it is probably that one receives a wage of $17 per hour minimum. I must add, I have never had any kind of emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. You should find these records somewhere inside “Contact Us” section in the website.
It doesn’t seem fair folks don’t have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending most of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. ” A good a reaction to this is just not “I’m trying to find a job. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training is the necessary steps to maintain the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can get a lot more done in a calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Drugs might be ordered by simply entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click in the mouse button. Make sure that you take the time to ask about a less expensive version so that they will confirm the list.
It might be used by fraudsters gain access to your accounts at a variety of financial institutions. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy knowning that it is a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. If you receive prescriptions every month make sure your pharmacy has your most up to date prescription insurance information.
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due for the perceived utilization of any medical device, whether it’s a pill or perhaps a syringe. To find degree programs that train you to get a career as a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy around possible.
An online pharmacy is quite a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart solution on a secure server. Use those outlines as being a roadmap to aid you study for that pharmacy tech certification test.
An online pharmacy is fairly a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. Important point to become noticed is the fact that cost can’t always be the first consideration. An one that finds work with this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to do work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images how the latter uses as bases for his or her diagnoses.
An online pharmacy is very a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart application on a secure server. Strong customer support skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
An online pharmacy is quite a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart software on a good server. Strong customer service skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or other drug information. As a smaller entrepreneur, when is it time to boost prices like Netflix. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Location and the form of employer are the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. I must add, I have never had any kind of emotional disorder within my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. They are also responsible for inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to boost the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can get yourself a lot more done in the calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Drugs could be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click of the mouse button. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you ought to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim the websites feel safe for paying online.
It could be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at a number of financial institutions. I must add, I have never had just about any emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to boost the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
By giving your pharmacy the complete name of your medication you’ll be able to better safe guard your health. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English like a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are kept in (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can get a lot more done in the calm friendly manner then you ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country could possibly be another, as well as the avian temperature may be the other. It is very important that the internet doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly provides medicine.
The live answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. The holding, the transfers, the new rules as well as the mail-order requirements. The massive rise in people online for many of the shopping and everyday needs has led to many pharmacies having a web site built, where they provide numerous services which may help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
#speman
By giving your pharmacy the complete name of one’s medication you are able to better safe guard your health. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart software on a good server. This is really a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) prior to the next open enrollment season in November.
To get the most out with the card, use it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. College pre-pharmacy study as little as a day or two which enable it to still pass the exam. So like a buyer, you will need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
We were going on the big city to determine a doctor, so it made sense. Drugs could be ordered by just entering the pharmacy website and placing an order which has a click from the mouse button. It is crucial that the internet doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
If you happen to be disabled based on federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally may have your student loans discharged. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude can’t help the situation. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
If you are disabled based on federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally may have your student loans discharged. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease inside shopping center that’s about being developed in the heart of Makati. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Important point to be noticed is always that cost can’t always be the first consideration. Strong customer care skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can obtain a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist around the counter. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country could possibly be another, and the avian temperature will be the other. It is extremely important that the online doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, side effects, and other drug information. As a little entrepreneur, when is it time to raise prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
This online pharmacy is really very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a little entrepreneur, just when was it time to improve prices like Netflix. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform lot a lot more than provide medications to patients.
Location and the sort of employer would be the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a new policy which it can be a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. You should find this info somewhere inside “Contact Us” section from the website.
The moon sheds her subtle affect on all on this, adding on the variables. You may also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So being a buyer, you need to identify a realistic online pharmacy that is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Location and the sort of employer would be the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician have to have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. You should find this information somewhere inside “Contact Us” section of the website.
This online pharmacy is basically very ideal for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude can’t help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
If you might be disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you definitely generally might have your student loans discharged. As a tiny entrepreneur, just when was it time to boost prices like Netflix. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career like a PT because it helps in making one more qualified when they apply for promotion. To find degree programs that train you for any career being a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. So like a buyer, you need to identify an authentic online pharmacy which is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
An online pharmacy is quite a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing first of all, additionally it is constantly changing. Strong customer support skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of your pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or any other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease inside the shopping center which was about to get developed within the heart of Makati. After you filled in the account, you are going to now go with a payment scheme.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. As a tiny entrepreneur, just when was it time to improve prices like Netflix. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
There are two ways to become a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered through your state. These will be the pharmacist who works as a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of the time within the other areas of pharmacy. So as a buyer, you’ll need to identify an authentic online pharmacy that’s licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can have a lot more done in a calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. ” A good response to this isn’t “I’m trying to find a job. It is extremely important that the internet doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained just a bit of Schadenfreude. I must add, I have never had virtually any emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to enhance the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, or another drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease within the shopping center that’s about to be developed inside the heart of Makati. After you filled in the account, you will now select a payment scheme.
The pharmaceutical industry especially do not want to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatments for clients due towards the perceived using any medical device, be it a pill or even a syringe. To find degree programs that train you for the career like a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. So being a buyer, you may need to identify a realistic online pharmacy that’s licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
If you are disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally might have your student loans discharged. Ask the managers with the places where you enjoy shopping if they feature these types of programs, in the event you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include providing the precise measurements of oxygen or other types of gas concentrations in the patient’s blood along with measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
It is essential to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives this kind of low wage and that when working in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one gets to be a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. Fear not, after a while you will know just how to handle different kinds of problems that can come about. If you receive prescriptions from month to month make sure your pharmacy has your most current prescription insurance information.
We were going for the big city to see a doctor, therefore it made sense. Drugs might be ordered by simply entering the pharmacy website and placing an order using a click in the mouse button. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you have to be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim that these websites feel at ease for paying online.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, and other drug information. Ask the managers in the places where you enjoy shopping if they provide these varieties of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, side effects, and other drug information. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are required to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. According on the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot a lot more than provide prescription medications to patients.
An online pharmacy is pretty a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart on a safe and secure server. Strong customer support skills really are a must when handling the hectic pace of a pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. As a tiny entrepreneur, when was it time to improve prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse management of clients due for the perceived utilization of any medical device, be it a pill or even a syringe. To find degree programs that train you for any career as a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy as much as possible.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due for the perceived use of any medical device, be it a pill or perhaps a syringe. These will be the pharmacist who works being a professor or lecture in almost any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time inside the other areas of pharmacy. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information into the computer.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, side effects, or any other drug information. As a smaller entrepreneur, when is it time to increase prices like Netflix. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include supplying the precise measurements of oxygen or other types of gas concentrations inside the patient’s blood along with measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
To get the most out with the card, use it every visit whilst track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. To find degree programs that train you to get a career like a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. So like a buyer, you may need to identify a realistic online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
To maximum benefit out of the card, utilize it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. You might additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
CVS Pharmacy must depend on prescription drug sales to stay in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t must add a massive markup to the prescribed drugs they sell. ” A good a reaction to this is not “I’m searching for a job. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe include the two names you need to be looking out for as well since these names will proclaim why these websites are safe for paying online.
The moon sheds her subtle impact on all on this, adding on the variables. To find degree programs that train you for any career like a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. So as being a buyer, you will need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that’s licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
We were going for the big city to see a doctor, therefore it made sense. When all factors are considered, however, I would ought to say that this prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. In order to register while using GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain either a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
The moon sheds her subtle influence on all of this, adding towards the variables. These will be the pharmacist who works as a professor or lecture in almost any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time inside other areas of pharmacy. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy up to possible.
To make the most out with the card, put it to use every visit and make track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. You might also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better chances of being successful.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Ask the managers from the places in places you enjoy shopping if they have these kinds of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained just a bit of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech about it new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy understanding that it is often a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these details somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section in the website.
We were going for the big city to determine a doctor, therefore it made sense. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, which is a fact. Make sure that you take enough time to ask about a more affordable version so they will confirm the list.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending the entire content of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. ” A good reaction to this isn’t “I’m looking for a job. It is essential that the web doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart application on a good server. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions obviously called qualifying life events or QLEs) prior to the next open enrollment season in November.
Also, look for your bargain table at the front of the store packed with items around 50 percent off of the regular price. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart software on a secure server. Strong customer care skills really are a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must spend the money for entire cost out-of-pocket. As a tiny entrepreneur, when is it time to increase prices like Netflix. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other kinds of gas concentrations inside the patient’s blood as well as measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules along with the mail-order requirements. Use those outlines as a roadmap to help you study for your pharmacy tech certification test.
The certification does play a huge role in making a rewarding career as a PT as it helps in making one more qualified after they apply for promotion. These will be the pharmacist who works as a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of the time inside the other areas of pharmacy. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information into the computer.
The pharmaceutical industry especially do not want to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatments for clients due towards the perceived utilization of any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or even a syringe. These are the pharmacist who works as a professor or lecture in almost any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent with their time inside other areas of pharmacy. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy around possible.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can have a lot more done in a calm friendly manner then you ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. The local temperature with the medicine producing country is one along with the other country might be another, and also the avian temperature may be the other. Most drugs need to get stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
CVS Pharmacy must rely on prescription drug sales to remain in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add a huge markup to the prescribed drugs they sell. Drugs may be ordered by just entering the pharmacy website and placing an order with a click with the mouse button. Make certain you take some time to ask about a more affordable version so that they will confirm the list.
An online pharmacy is fairly a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. Before taking any exams required by their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. An individual that finds work on this profession can be described as a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that provides the doctors with scanned images that the latter use as bases for their diagnoses.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse management of clients due to the perceived using any medical device, it could be a pill or a syringe. To find degree programs that train you for the career being a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we now have better probability of being successful.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs available for purchase and that they are burdened with spending most of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. When all factors are considered, however, I would need to say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are quite comparable. In order to register while using GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain the 3 Level 3 qualifications.
#proventil
To maximum benefit out in the card, use it every visit and keep track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. College pre-pharmacy study as little like a day or two and can still pass the exam. So being a buyer, you need to identify a realistic online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
This online pharmacy is actually very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease within the shopping center that’s about to be developed within the heart of Makati. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform lot a lot more than provide medications to patients.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or any other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease in the shopping center that was about to become developed within the heart of Makati. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and invented exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) should be completed and aid is granted dependant on student need, tuition rates in the college, as well as other factors. When I asked the tech concerning this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy understanding that it can be a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. If you receive prescriptions on a monthly basis make sure your pharmacy has your most current prescription insurance information.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams required by their state, they have to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. An one that finds work in this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to do work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that delivers the doctors with scanned images how the latter will use as bases for diagnoses.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. As a smaller entrepreneur, when is it time to boost prices like Netflix. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot more than provide prescriptions to patients.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) has to be completed and aid is granted based upon student need, tuition rates at the college, and other factors. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy which it is really a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of your respective medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart on a secure server. Strong customer service skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of your pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or any other drug information. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot greater than provide prescription medications to patients.
This online pharmacy is actually very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a tiny entrepreneur, when is it time to boost prices like Netflix. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that these are burdened with spending the rest of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, what a fact. It is crucial that the web doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
This online pharmacy is basically very ideal for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Ask the managers with the places in which you enjoy shopping if they provide these varieties of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. After you filled in the account, you are going to now pick a payment scheme.
There are two ways being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. You may also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. There is absolutely no difference between ordering drugs from a drugstore in the United States than through a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
Location and the type of employer would be the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. The last volume of a certified local pharmacy professional training course takes a 12 month preparation software in addition to as soon as the completing the specific tutorials you could purchase an associates education. They are also responsible for inspecting the operational treatments for dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to boost the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
The live answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Before taking any exams necessary for their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are kept in (with minor exceptions of course called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can certainly be some times, you can get a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner then you ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. Drugs could be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click of the mouse button. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you have to be looking out for as well since these names will proclaim these websites feel safe for paying online.
An online pharmacy is fairly a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing in the first place, plus it is constantly changing. Use those outlines being a roadmap to help you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted dependant on student need, tuition rates on the college, along with other factors. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. You should find this information somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section from the website.
The certification does play a huge role in making a rewarding career as a PT because it helps for making one more qualified whenever they apply for promotion. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two which enable it to still pass the exam. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information into the computer.
It is vital to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives a real low wage knowning that when employed in private pharmacies, it is almost certainly that one gets to be a wage of $17 hourly minimum. When I asked the tech about it new action she stated that yes, it is a new policy knowning that it is often a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
In order to be eligible for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) has to be completed and aid is granted based upon student need, tuition rates with the college, along with other factors. The pharmacist technician have to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to some patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which can be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which can be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
It might be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at a number of financial institutions. The very last volume of a certified local pharmacy professional program takes a twelve month preparation software in addition to as soon because the completing the actual tutorials you could purchase an associates education. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and can include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Location and the sort of employer would be the final factors in determining how much pharmacists make. I must add, I have never had just about any emotional disorder within my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. The application deadline is late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
While there is often a small chance you can get laid off (for instance, if your chain supermarket closes some stores) you must not have much problem finding another job. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, that’s a fact. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you need to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim why these websites are safe for paying online.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Insurance is confusing to start with, additionally it is constantly changing. Strong customer care skills certainly are a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
In order to qualify for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted in relation to student need, tuition rates at the college, along with other factors. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy which it can be a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. If you receive prescriptions monthly make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, and other drug information. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and invented exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs available for purchase and that these are burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. Drugs could be ordered just by entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click in the mouse button. It is extremely important that the online doctor exactly understands exactly what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart application on a good server. This is a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions needless to say called qualifying life events or QLEs) before the next open enrollment season in November.
We were going to the big city to see a doctor, therefore it made sense. ” A good a reaction to this just isn’t “I’m trying to find a job. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you should be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim the websites are safe for paying online.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease inside shopping center which was about to get developed inside heart of Makati. After you filled in the account, you are going to now select a payment scheme.
Location and the kind of employer would be the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. I must add, I have never had any type of emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and can include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
We were going towards the big city to find out a doctor, so that it made sense. Drugs may be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click of the mouse button. Most drugs need to get stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training is the necessary steps to maintain the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
#florinef
Most patients were paying big money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must give the entire cost out-of-pocket. Ask the managers with the places in which you enjoy shopping if they provide these varieties of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
It is essential to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage knowning that when working in private pharmacies, it is almost certainly that one turns into a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. The final volume of the certified local pharmacy professional study course takes a 12 month preparation software as well as as soon because completing the specific tutorials you may purchase an associates education. You should find these records somewhere inside “Contact Us” section from the website.
The live answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules along with the mail-order requirements. An individual that finds work with this profession can be described as a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images that the latter will use as bases for his or her diagnoses.
It can be used by fraudsters to gain access to your accounts at a number of financial institutions. The pharmacist technician have to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to some patient or customer. If you get prescriptions monthly make sure your pharmacy has your most current prescription insurance information.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted based upon student need, tuition rates on the college, and other factors. When I asked the tech concerning this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy which it can be a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. They are also to blame for inspecting the operational treatments for dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to enhance the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
The answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules and also the mail-order requirements. The massive boost in people online for many of these shopping and day by day needs has generated many pharmacies having a website built, where they provide numerous services which can help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your neighborhood pharmacy.
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due for the perceived utilization of any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or possibly a syringe. These are the pharmacist who works being a professor or lecture in a medical college; they spend around 50 per cent with their time in the other areas of pharmacy. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy up to possible.
An online pharmacy is quite a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing to start with, additionally it is constantly changing. An one that finds work with this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that delivers the doctors with scanned images the latter use as bases for his or her diagnoses.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs available for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending the rest of their life worrying about something that could affect their survival like this. Drugs could be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click of the mouse button. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one in the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to hold the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can get yourself a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist around the counter. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one and also the other country may be another, along with the avian temperature is the other. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you ought to be looking out for as well since these names will proclaim these websites are secure for paying online.
It might be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at numerous financial institutions. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. The application deadline is at late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due to the perceived utilization of any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or possibly a syringe. To find degree programs that train you to get a career like a pharmacy technician, you are able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. They could also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can get a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. It is very important that the internet doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
It is vital to note that every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage knowning that when employed in private pharmacies, it is probably that one receives a wage of $17 hourly minimum. Fear not, as time passes you will know exactly how to handle different forms of problems that comes about. You should find this info somewhere inside “Contact Us” section in the website.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, and other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a space to lease within the shopping center which was about being developed within the heart of Makati. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot over provide medications to patients.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered through your state. The above image shows that the secure protocol ( will be used with the fraudster. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy up to possible.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must spend the money for entire cost out-of-pocket. Ask the managers of the places in places you enjoy shopping if they provide these types of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. According on the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform lot over provide prescriptions to patients.
It doesn’t seem fair folks don’t have cheap drugs available for purchase and that they are burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something that could affect their survival like this. The local temperature from the medicine producing country is one and the other country could be another, as well as the avian temperature will be the other. Make sure you take time to ask about a cheaper version so they really will look at the list.
While there is a small chance you could get laid off (by way of example, if the chain supermarket closes some stores) you shouldn’t have much problem finding another job. ” A good reaction to this isn’t “I’m trying to find a job. In order to register with the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain sometimes a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or other drug information. Ask the managers in the places in which you enjoy shopping if they have these kinds of programs, should you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. After you completed the account, you may now decide on a payment scheme.
An online pharmacy is quite a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they should pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are kept in (with minor exceptions of course called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of one’s medication you are able to better safe guard your health. Important point to become noticed is always that cost can’t continually be the first consideration. Use those outlines being a roadmap to help you study to the pharmacy tech certification test.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. As a smaller entrepreneur, just when was it time to raise prices like Netflix. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot a lot more than provide prescription medications to patients.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. As a little entrepreneur, when is it time to raise prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.info/vi/join?ref=T7KCZASX
An online pharmacy is fairly a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart software on a good server. An individual that finds work with this profession can be described as a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment providing you with the doctors with scanned images that this latter make use of as bases for their diagnoses.
It can be used by fraudsters to gain access to your accounts at many different financial institutions. The last volume of a certified local pharmacy professional program takes a 12 month preparation software and also as soon because the completing the particular tutorials you may purchase an associates education. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and can include streptococci, that happen to be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which can be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatments for clients due on the perceived using any medical device, be it a pill or even a syringe. The above image shows that the secure protocol ( has been used with the fraudster. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
By giving your pharmacy the precise name of your respective medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Important point to get noticed is that cost can’t always be the first consideration. Use those outlines as being a roadmap to help you you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can obtain a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. When all factors are viewed, however, I would have to say how the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. Make certain that you take the time to ask about a less expensive version so that they will look at the list.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can have a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Factors staying taught in institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. In order to register using the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain the 3 Level 3 qualifications.
There are two ways for being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. College pre-pharmacy study as little like a day or two and will still pass the exam. So as a buyer, you will need to identify an authentic online pharmacy which is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Important point to be noticed is the fact that cost can’t often be the first consideration. An one that finds work within this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that delivers the doctors with scanned images that this latter uses as bases for their diagnoses.
An online pharmacy is pretty a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing in the first place, additionally it is constantly changing. The massive surge in people using the internet for many of the shopping and day by day needs has generated many pharmacies having a website built, where they feature numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
While there is often a small chance you have access to laid off (for example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you should not have much problem finding another job. Drugs might be ordered by just entering the pharmacy website and placing an order using a click of the mouse button. Make certain that you take some time to ask about a more affordable version so that they will look into the list.
#amaryl
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. The massive increase in people online for many of the shopping and day to day needs has generated many pharmacies having an online site built, where they feature numerous services which may help you avoid making unnecessary trips to the local pharmacy.
This online pharmacy is actually very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
To make the most out with the card, utilize it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. The above image shows which a secure protocol ( is being used with the fraudster. There is actually no difference between ordering drugs from your drugstore inside the United States than through a Canada pharmacy except for your price.
The moon sheds her subtle relation to all of the, adding on the variables. To find degree programs that train you for any career being a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. So as being a buyer, you need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Location and the sort of employer include the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to a patient or customer. The application deadline is within late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, and other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease within the shopping center that’s about to become developed inside heart of Makati. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other forms of gas concentrations inside the patient’s blood in addition to measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
CVS Pharmacy must depend on prescription drug sales to keep in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t need to add a massive markup to the prescription drugs they sell. When all factors are considered, however, I would must say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. It is essential that the online doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
To obtain the most out of the card, utilize it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. To find degree programs that train you to get a career like a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve got better chances of being successful.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are needed to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) should be completed and aid is granted dependant on student need, tuition rates in the college, and other factors. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a whole new policy and that it is really a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career like a PT because it helps for making one more qualified after they apply for promotion. The above image shows which a secure protocol ( will be used with the fraudster. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy up to possible.
An online pharmacy is pretty a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. Important point being noticed is that cost can’t often be the first consideration. This is a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a brand new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions needless to say called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
If you are disabled based on federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you definitely generally can have your student loans discharged. As a small entrepreneur, when was it time to increase prices like Netflix. After you filled in the account, you will now pick a payment scheme.
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or any other drug information. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude can’t help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career as a PT because it helps to produce one more qualified once they apply for promotion. To find degree programs that train you to get a career like a pharmacy technician, you can check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we have better probability of being successful.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can certainly be some times, you can get yourself a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist around the counter. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you need to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim that these websites feel safe for paying online.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. The holding, the transfers, the new rules and the mail-order requirements. Use those outlines being a roadmap to help you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
While there is really a small chance you can get laid off (for instance, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you shouldn’t have much problem finding another job. Drugs could be ordered by simply entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click of the mouse button. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one in the things pharmacists learn in pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
It is important to note that not every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage understanding that when in private pharmacies, it is probably that one gets to be a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. Fear not, after a while you will know exactly how to handle different forms of problems that comes about. If you get prescriptions on a monthly basis make sure your pharmacy has your most current prescription insurance information.
The certification does play a huge role in making a rewarding career as being a PT because it helps to make one more qualified whenever they apply for promotion. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( has used through the fraudster. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we now have better chances of being successful.
It doesn’t seem fair people don’t have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they are burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about a thing that could affect their survival like this. ” A good reply to this isn’t “I’m seeking a job. Make sure you take enough time to ask about a cheaper version so they will look at the list.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. The holding, the transfers, the new rules and the mail-order requirements. This is a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions of course called qualifying life events or QLEs) before the next open enrollment season in November.
It might be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at numerous financial institutions. The last volume of your certified local pharmacy professional program takes a twelve month preparation software as well as as soon because the completing this tutorials you could possibly purchase an associates education. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which can be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which can be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
To make the most out of the card, put it to use every visit and make track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. These include the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent with their time inside the other areas of pharmacy. They could also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can obtain a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner then you ever will accomplish by pounding your fist around the counter. ” A good a reaction to this just isn’t “I’m searching for a job. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you have to be looking out for as well because these names will proclaim these websites feel at ease for paying online.
While there is a small chance you can get laid off (for example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you must not have much problem finding another job. Drugs could be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click from the mouse button. In order to register with all the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain sometimes a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that these are burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something that could affect their survival like this. When all factors are thought, however, I would must say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. Make sure you take time to ask about a more affordable version so they will look at the list.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can get yourself a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. Factors staying taught in universities regularly variations, that’s a fact. Most drugs need to be stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training may be the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, and other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que space to lease inside the shopping center that has been about to get developed within the heart of Makati. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other kinds of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood as well as measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
It may be used by fraudsters gain access to your accounts at many different financial institutions. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to a patient or customer. The application deadline is in late April, but it’s best to apply much sooner.
Location and the type of employer include the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed by way of a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. You should find these records somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section with the website.
It is essential to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage which when doing work in private pharmacies, it is probably that one turns into a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria you need to include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
CVS Pharmacy must rely on prescription drug sales to remain in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t need to add a tremendous markup to the medications they sell. When all factors are believed, however, I would must say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy can be comparable. Most drugs need to be stored at exact temperatures, so one from the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training is the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
#levlen
We were going towards the big city to see a doctor, in order that it made sense. Drugs could be ordered by just entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click from the mouse button. Make sure that you take enough time to ask about a cheaper version so that they will confirm the list.
#actonel
It is very important to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage knowning that when employed in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one receives a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. Fear not, after a while you will know just how to handle different types of problems that can come about. They are also in charge of inspecting the operational control over dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to enhance the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
This online pharmacy is actually very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are required to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform lot greater than provide prescription drugs to patients.
Also, look for the bargain table close to the front from the store full of items up to 50 percent over regular price. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart on a good server. The massive boost in people online for many of the shopping and day to day needs has resulted in many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they have numerous services which can help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
It might be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at a variety of financial institutions. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy which it is often a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. You should find this info somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section from the website.
Most patients were paying a high income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they’d not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease within the shopping center that has been about to become developed inside the heart of Makati. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
We were going for the big city to see a doctor, so it made sense. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country could possibly be another, as well as the avian temperature will be the other. Make certain that you take enough time to ask about a less expensive version in order that they will look at the list.
The moon sheds her subtle impact on all with this, adding to the variables. College pre-pharmacy study as little as a day or two and can still pass the exam. So as a buyer, you may need to identify a traditional online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, or any other drug information. Ask the managers in the places in places you enjoy shopping if they offer these forms of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot over provide medications to patients.
An online pharmacy is pretty a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing first of all, and yes it is constantly changing. Use those outlines like a roadmap to help you study to the pharmacy tech certification test.
If you’re disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you generally might have your student loans discharged. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or just being rude won’t help the situation. After you completed the account, you may now select a payment scheme.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease in the shopping center that was about being developed inside the heart of Makati. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other forms of gas concentrations in the patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
The moon sheds her subtle relation to all of the, adding to the variables. You might additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So as a buyer, you may need to identify a realistic online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Also, look to the bargain table close to the front of the store full of items approximately 50 percent over regular price. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart on a secure server. The massive increase in people creating an online business for many with their shopping and day to day needs has generated many pharmacies having a website built, where they provide numerous services which may help you avoid making unnecessary trips to any local pharmacy.
It might be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at a variety of financial institutions. I must add, I have never had virtually any emotional disorder within my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and can include streptococci, which are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or any other drug information. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are required to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or any other drug information. Ask the managers in the places in places you enjoy shopping if they have these varieties of programs, in the event you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. After you done the account, you may now select a payment scheme.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing with a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. I must add, I have never had any type of emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria you need to include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which can be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
It is important to note that not every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage and that when working in private pharmacies, it is most likely that one receives a wage of $17 per hour minimum. The pharmacist technician will need to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to a patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and can include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
While there is a small chance you can get laid off (as an example, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you should not have much problem finding another job. Drugs may be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order with a click from the mouse button. Make certain you take enough time to ask about a cheaper version so they will look into the list.
Location and the sort of employer include the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. I must add, I have never had any type of emotional disorder within my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. You should find this information somewhere in the “Contact Us” section with the website.
The answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. The holding, the transfers, the new rules and the mail-order requirements. The massive surge in people using the internet for many with their shopping and day by day needs has triggered many pharmacies having a web site built, where they offer numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
Most patients were paying a high income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. Ask the managers with the places that you enjoy shopping if they feature these types of programs, in the event you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other types of gas concentrations in the patient’s blood in addition to measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
This online pharmacy is basically very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a tiny entrepreneur, when is it time to boost prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Ask the managers in the places in which you enjoy shopping if they have these varieties of programs, in the event you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include supplying the precise measurements of oxygen or other forms of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
While there is often a small chance you have access to laid off (as an example, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you must not have much problem finding another job. When all factors are thought, however, I would ought to say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy can be comparable. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one in the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training may be the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or any other drug information. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude can’t help the situation. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform lot over provide prescription medications to patients.
The live answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Important point to become noticed is cost can’t always be the first consideration. The massive surge in people using the internet for many of the shopping and day by day needs has resulted in many pharmacies having an online site built, where they provide numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
By giving your pharmacy the precise name of the medication you’ll be able to better safe guard your health. Before taking any exams required by their state, they should pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. The massive increase in people online for many of their shopping and daily needs has resulted in many pharmacies having a web site built, where they feature numerous services which can help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
It is very important to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage knowning that when in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one turns into a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. The very last volume of a certified local pharmacy professional training course takes a one year preparation software and also as soon because the completing the actual tutorials you might purchase an associates education. If you will get prescriptions monthly make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing using a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. Fear not, with time you will know precisely how to handle different forms of problems that will come about. They are also in charge of inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to boost the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can have a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. The local temperature with the medicine producing country is one and the other country could possibly be another, and the avian temperature could be the other. In order to register while using GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain the 3 Level 3 qualifications.
An online pharmacy is very a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. The holding, the transfers, the newest rules as well as the mail-order requirements. The massive surge in people creating an online business for many of these shopping and day to day needs has triggered many pharmacies having a web site built, where they offer numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to the local pharmacy.
#silvitra
There are two ways being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered because of your state. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two and can still pass the exam. There is actually no difference between ordering drugs coming from a drugstore in the United States than through a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or another drug information. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are required to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can have a lot more done in a calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one and also the other country may be another, as well as the avian temperature will be the other. It is essential that the online doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
We were going on the big city to determine a doctor, therefore it made sense. Factors staying taught in universities regularly variations, which is a fact. It is crucial that the net doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
The moon sheds her subtle relation to all on this, adding on the variables. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two and can still pass the exam. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy just as much as possible.
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of your respective medication you are able to better safe guard your health. Insurance is confusing in the first place, and it also is constantly changing. Use those outlines being a roadmap to aid you study to the pharmacy tech certification test.
CVS Pharmacy must depend upon prescription drug sales to remain in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t need to add a massive markup to the prescription drugs they sell. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, that’s a fact. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you have to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim that these websites are secure for paying online.
An online pharmacy is quite a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart solution on a secure server. Use those outlines being a roadmap to help you you study to the pharmacy tech certification test.
There are two ways being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered by your state. These will be the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time in the other areas of pharmacy. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy as much as possible.
This online pharmacy is absolutely very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que space to lease inside the shopping center that’s about being developed inside the heart of Makati. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
It can be used by fraudsters to get into your accounts at a number of financial institutions. The final volume of a certified local pharmacy professional study course takes a one year preparation software along with as soon because completing the specific tutorials you could purchase an associates education. You should find this information somewhere inside “Contact Us” section of the website.
It is vital to note that does not every pharmacy technician receives this kind of low wage which when in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one turns into a wage of $17 per hour minimum. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy which it is a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to enhance the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Also, look for that bargain table near the front of the store packed with items approximately 50 percent off the regular price. The holding, the transfers, the brand new rules and also the mail-order requirements. Strong customer satisfaction skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of your pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
To make the most out of the card, apply it every visit and make track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. College pre-pharmacy study as little being a day or two and may still pass the exam. So like a buyer, you will need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
The moon sheds her subtle relation to all of this, adding for the variables. These include the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent with their time inside the other areas of pharmacy. There is absolutely no difference between ordering drugs coming from a drugstore in the United States than by way of a Canada pharmacy except for your price.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. To find degree programs that train you for the career being a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy just as much as possible.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Important point to get noticed is always that cost can’t often be the first consideration. An person that finds work within this profession can be described as a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to perform work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that provides the doctors with scanned images that the latter use as bases for their diagnoses.
If you are disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally will surely have your student loans discharged. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude will not help the situation. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
The moon sheds her subtle affect on all on this, adding on the variables. You might additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. There is basically no difference between ordering drugs from your drugstore in the United States than by having a Canada pharmacy except to the price.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing to begin with, and yes it is constantly changing. An individual who finds work with this profession can be described as a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to perform work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that provides the doctors with scanned images the latter make use of as bases for his or her diagnoses.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude can’t help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career being a PT since it helps to produce one more qualified once they apply for promotion. You may additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So as being a buyer, you need to identify an authentic online pharmacy which is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
The moon sheds her subtle influence on all with this, adding towards the variables. These would be the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time inside the other areas of pharmacy. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy just as much as possible.
In order to qualify for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) has to be completed and aid is granted based on student need, tuition rates in the college, and other factors. The pharmacist technician will need to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by way of a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. You should find this information somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section of the website.
We were going for the big city to see a doctor, so it made sense. Factors staying taught in universities regularly variations, that’s a fact. In order to register with all the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain whether 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules along with the mail-order requirements. Strong customer service skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of a pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
The certification does play a huge role in making a rewarding career being a PT because it helps for making one more qualified when they apply for promotion. You may also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information into the computer.
Also, look to the bargain table close to the front of the store packed with items up to 50 percent over regular price. The holding, the transfers, the new rules as well as the mail-order requirements. An person that finds work in this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images how the latter use as bases for their diagnoses.
The moon sheds her subtle impact on all on this, adding towards the variables. College pre-pharmacy study as little being a day or two and can still pass the exam. If possible try to use the same pharmacy around possible.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart on a good server. An individual who finds work with this profession can be considered a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that provides the doctors with scanned images how the latter uses as bases because of their diagnoses.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can have a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, which is a fact. It is crucial that the web doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly provides medicine.
While there is a small chance you can get laid off (for example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you must not have much problem finding another job. Drugs can be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click with the mouse button. Make certain that you take the time to ask about a cheaper version so they will look at the list.
Location and the form of employer will be the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. Fear not, after a while you will know the best way to handle different types of problems that may come about. If you receive prescriptions on a monthly basis make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
#propecia
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs available to them for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending the rest of their life worrying about a thing that could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in institutions regularly variations, this is a fact. In order to register while using GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain whether 3 Level 3 qualifications.
While there is often a small chance you can get laid off (as an example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you must not have much problem finding another job. Drugs might be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order which has a click with the mouse button. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you need to be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim the websites feel at ease for paying online.
CVS Pharmacy must depend upon prescription drug sales to be in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add a tremendous markup to the prescribed drugs they sell. Drugs can be ordered by just entering the pharmacy website and placing an order with a click of the mouse button. In order to register with the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain sometimes a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
It is important to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage and that when in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one gets to be a wage of $17 hourly minimum. The pharmacist technician have to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by way of a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to your patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and can include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
This online pharmacy is actually very ideal for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Ask the managers of the places in which you enjoy shopping if they provide these kinds of programs, in the event you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. After you done the account, you may now pick a payment scheme.
While there is often a small chance you could get laid off (by way of example, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you mustn’t have much problem finding another job. ” A good reply to this isn’t “I’m looking for a job. Make certain you take enough time to ask about a less expensive version so they will look at the list.
It is essential to note that every pharmacy technician receives this kind of low wage which when working in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one gets to be a wage of $17 per hour minimum. The last volume of the certified local pharmacy professional training program takes a twelve month preparation software and also as soon because the completing the particular tutorials you might purchase an associates education. The application deadline is at late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams required by their state, they have to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English like a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. An individual who finds work in this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to do work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment providing you with the doctors with scanned images how the latter make use of as bases for diagnoses.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, side effects, or any other drug information. As a small entrepreneur, when was it time to raise prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and invented exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
While there is a small chance you have access to laid off (as an example, if the chain supermarket closes some stores) you mustn’t have much problem finding another job. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, that’s a fact. Make certain that you take the time to ask about a less expensive version in order that they will check the list.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, or other drug information. As a smaller entrepreneur, when was it time to raise prices like Netflix. According on the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot greater than provide medications to patients.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. The holding, the transfers, the brand new rules along with the mail-order requirements. Strong customer care skills certainly are a must when handling the hectic pace of a pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing using a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. The pharmacist technician will need to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to your patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria you need to include streptococci, which can be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Important point to get noticed is always that cost can’t often be the first consideration. This is a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are stuck (with minor exceptions obviously called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
The certification does play a huge role in making a rewarding career being a PT since it helps to produce one more qualified after they apply for promotion. The above image shows which a secure protocol ( has been used by the fraudster. If possible try to use the same pharmacy up to possible.
An online pharmacy is very a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. Important point to be noticed is the fact that cost can’t always be the first consideration. An one that finds work within this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to do work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images the latter uses as bases for his or her diagnoses.
The moon sheds her subtle affect on all of the, adding on the variables. The above image shows a secure protocol ( has used with the fraudster. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in universities regularly variations, this is a fact. It is essential that the web doctor exactly understands exactly what the problem is and accordingly provides medicine.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they must pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Use those outlines as a roadmap to aid you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Most patients were paying a nice income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they’d not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude will not help the situation. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot greater than provide prescription drugs to patients.
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career as a PT mainly because it helps to produce one more qualified when they apply for promotion. To find degree programs that train you for the career being a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. They also can check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered because of your state. You may also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. There is absolutely no difference between ordering drugs from the drugstore inside United States than by having a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Important point to become noticed is that cost can’t be the first consideration. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are stuck (with minor exceptions obviously called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatments for clients due towards the perceived use of any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or perhaps a syringe. The above image shows which a secure protocol ( has been used with the fraudster. So as a buyer, you need to identify an authentic online pharmacy that’s licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
It may be used by fraudsters gain access to your accounts at a variety of financial institutions. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy knowning that it can be a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. They are also responsible for inspecting the operational control over dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
It doesn’t seem fair folks don’t have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending the rest of their life worrying about something that could affect their survival like this. When all factors are believed, however, I would have to say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy can be comparable. It is extremely important that the web doctor exactly understands exactly what the problem is and accordingly gives the medicine.
The moon sheds her subtle affect on all on this, adding for the variables. To find degree programs that train you for any career like a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. They could also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or other drug information. As a small entrepreneur, just when was it time to raise prices like Netflix. After you filled in the account, you may now go with a payment scheme.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can obtain a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one and also the other country might be another, as well as the avian temperature may be the other. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you should be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim the websites feel at ease for paying online.
This online pharmacy is really very ideal for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are needed to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
The pharmaceutical industry especially do not want to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due towards the perceived usage of any medical device, it could be a pill or even a syringe. The above image shows which a secure protocol ( has used with the fraudster. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy just as much as possible.
An online pharmacy is quite a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart software on a safe and secure server. An person that finds work within this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment providing you with the doctors with scanned images the latter use as bases because of their diagnoses.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs available to them for purchase and that these are burdened with spending the entire content of their life worrying about a thing that could affect their survival like this. The local temperature with the medicine producing country is one and also the other country may be another, as well as the avian temperature could be the other. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training is the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) has to be completed and aid is granted dependant on student need, tuition rates at the college, and other factors. I must add, I have never had any kind of emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. If you obtain prescriptions from month to month make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
There are two ways to become a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered because of your state. College pre-pharmacy study as little like a day or two which enable it to still pass the exam. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better probability of being successful.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart application on a safe and secure server. An person that finds work with this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment providing you with the doctors with scanned images that the latter make use of as bases because of their diagnoses.
If you might be disabled based on federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally may have your student loans discharged. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease within the shopping center that was about being developed inside the heart of Makati. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot over provide prescription medications to patients.
If you might be disabled in accordance with federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you generally will surely have your student loans discharged. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are needed to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. According on the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot more than provide medications to patients.
By giving your pharmacy the precise name of one’s medication you are able to better safe guard your health. Important point to be noticed is cost can’t always be the first consideration. This is really a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are stuck (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
We were going for the big city to see a doctor, so that it made sense. When all factors are thought, however, I would have to say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. It is crucial that the online doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly provides medicine.
This online pharmacy is basically very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a small entrepreneur, when was it time to improve prices like Netflix. According on the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot greater than provide medications to patients.
The moon sheds her subtle affect on all on this, adding to the variables. To find degree programs that train you for any career like a pharmacy technician, you are able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we have better chances of being successful.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Important point to be noticed is always that cost can’t often be the first consideration. This is really a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a brand new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
#zetia
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams necessary for their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. This is really a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can get a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. Drugs might be ordered just by entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click of the mouse button. It is crucial that the web doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly gives the medicine.
To get the most out with the card, utilize it every visit and keep track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. These will be the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of their time within the other areas of pharmacy. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better likelihood of being successful.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or another drug information. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
By giving your pharmacy the complete name of your respective medication you are able to better safe guard your health. Before taking any exams necessary for their state, they should pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English like a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. An person that finds work with this profession can be described as a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to perform work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment providing you with the doctors with scanned images the latter uses as bases for their diagnoses.
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of your medication you are able to better safe guard your health. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules and the mail-order requirements. The massive boost in people using the internet for many of their shopping and day to day needs has triggered many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they have numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or another drug information. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude won’t help the situation. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Location and the sort of employer will be the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. The application deadline is within late April, but it’s best to apply much sooner.
If you’re disabled based on federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally might have your student loans discharged. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude will not help the situation. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include supplying the precise measurements of oxygen or other kinds of gas concentrations inside the patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
The live answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing in the first place, plus it is constantly changing. This is really a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a brand new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are stuck (with minor exceptions needless to say called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
It is important to note that does not every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage and that when doing work in private pharmacies, it is most likely that one turns into a wage of $17 per hour minimum. The last volume of your certified local pharmacy professional program takes a 12 month preparation software as well as as soon since the completing the actual tutorials you could possibly purchase an associates education. If you get prescriptions on a monthly basis make sure your pharmacy has your most current prescription insurance information.
If you’re disabled in accordance with federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally might have your student loans discharged. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot over provide prescriptions to patients.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can get a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. When all factors are viewed, however, I would ought to say how the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are quite comparable. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one from the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to maintain the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that these are burdened with spending the entire content of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, what a fact. It is essential that the web doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
There are two ways being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two and will still pass the exam. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information to the computer.
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse management of clients due on the perceived utilization of any medical device, be it a pill or perhaps a syringe. These will be the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of their time within the other areas of pharmacy. They could also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a space to lease within the shopping center which was about to get developed in the heart of Makati. After you done the account, you are going to now pick a payment scheme.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or another drug information. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude can’t help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
While there is often a small chance you have access to laid off (for example, if your chain supermarket closes some stores) you should not have much problem finding another job. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. It is extremely important that the net doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly provides medicine.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered through your state. College pre-pharmacy study as little as a day or two which enable it to still pass the exam. There is really no difference between ordering drugs from a drugstore inside United States than via a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted in relation to student need, tuition rates at the college, along with other factors. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a whole new policy knowning that it is a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these details somewhere inside “Contact Us” section from the website.
It can be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at a number of financial institutions. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy which it is often a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these records somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section in the website.
The answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. The holding, the transfers, the brand new rules along with the mail-order requirements. Use those outlines like a roadmap to assist you study for your pharmacy tech certification test.
We were going to the big city to find out a doctor, so that it made sense. The local temperature from the medicine producing country is one and the other country may be another, and also the avian temperature will be the other. It is essential that the online doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly gives the medicine.
If you might be disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally might have your student loans discharged. As a smaller entrepreneur, when was it time to increase prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
It can be used by fraudsters to gain access to your accounts at many different financial institutions. When I asked the tech concerning this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy and that it is really a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. They are also to blame for inspecting the operational management of dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to enhance the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can certainly be some times, you can get a lot more done in the calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country could be another, and the avian temperature could be the other. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe include the two names you ought to be looking out for as well because these names will proclaim that these websites feel at ease for paying online.
In order to be eligible for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) has to be completed and aid is granted in relation to student need, tuition rates at the college, and other factors. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy understanding that it is often a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these details somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section from the website.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, side effects, or any other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que space to lease inside the shopping center that was about to be developed inside the heart of Makati. After you filled out the account, you may now go with a payment scheme.
CVS Pharmacy must count on prescription drug sales to be in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t must add a massive markup to the medications they sell. The local temperature with the medicine producing country is one along with the other country could possibly be another, and also the avian temperature is the other. In order to register using the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain either a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Also, look for that bargain table close to the front with the store full of items approximately 50 percent from the regular price. The holding, the transfers, the brand new rules and the mail-order requirements. Strong customer care skills certainly are a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
It is very important to note that does not every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage which when working in private pharmacies, it is most likely that one gets to be a wage of $17 hourly minimum. The last volume of the certified local pharmacy professional program takes a 12 month preparation software in addition to as soon as the completing the actual tutorials you could purchase an associates education. If you will get prescriptions monthly make sure your pharmacy has your most up to date prescription insurance information.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing which has a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech concerning this new action she stated that yes, it is a whole new policy and that it is really a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. You should find this info somewhere within the “Contact Us” section of the website.
If you are disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally will surely have your student loans discharged. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude won’t help the situation. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
#atorlip-10
There are two ways being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered because of your state. These would be the pharmacist who works as being a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time inside the other areas of pharmacy. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we have better chances of being successful.
If you happen to be disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally may have your student loans discharged. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are needed to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
We were going to the big city to determine a doctor, so that it made sense. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one and also the other country could be another, along with the avian temperature will be the other. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you ought to be looking out for as well since these names will proclaim the websites feel at ease for paying online.
To get the most out in the card, use it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( will be used with the fraudster. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy just as much as possible.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they should pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English like a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. This is often a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions of course called qualifying life events or QLEs) before the next open enrollment season in November.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing using a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. Fear not, eventually you will know exactly how to handle different kinds of problems that may come about. They are also in charge of inspecting the operational treatments for dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing which has a write-up that contained just a bit of Schadenfreude. I must add, I have never had any kind of emotional disorder during my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. You should find these records somewhere within the “Contact Us” section from the website.
The answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English like a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Strong customer service skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Also, look for the bargain table nearby the front of the store packed with items approximately 50 percent from the regular price. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart application on a safe and secure server. Use those outlines being a roadmap to help you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, or any other drug information. As a little entrepreneur, when is it time to boost prices like Netflix. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other types of gas concentrations in the patient’s blood in addition to measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due to the perceived usage of any medical device, it could be a pill or possibly a syringe. These include the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of the time within the other areas of pharmacy. If possible try to use the identical pharmacy as much as possible.
It doesn’t seem fair folks don’t have cheap drugs available to them for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending the entire content of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. ” A good response to this is not “I’m searching for a job. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you have to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim these websites feel safe for paying online.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. The holding, the transfers, the new rules as well as the mail-order requirements. The massive increase in people online for many of these shopping and day to day needs has resulted in many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they feature numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
This online pharmacy is basically very great for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
CVS Pharmacy must depend on prescription drug sales to keep in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add a massive markup to the medications they sell. Factors staying taught in universities regularly variations, which is a fact. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one in the things pharmacists learn in pharmaceutical quality training will be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Most patients were paying a high income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude can’t help the situation. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that they are burdened with spending most of their life worrying about a thing that could affect their survival like this. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one along with the other country could be another, as well as the avian temperature could be the other. Most drugs need to get stored at exact temperatures, so one in the things pharmacists learn in pharmaceutical quality training may be the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
The answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. This is often a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a brand new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are located in (with minor exceptions obviously called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
While there is often a small chance you can get laid off (for example, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you mustn’t have much problem finding another job. The local temperature with the medicine producing country is one and the other country might be another, and also the avian temperature is the other. Make sure that you take enough time to ask about a cheaper version in order that they will confirm the list.
CVS Pharmacy must count on prescription drug sales to keep in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t need to add a massive markup to the medications they sell. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country may be another, as well as the avian temperature will be the other. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training will be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can have a lot more done in a calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, which is a fact. In order to register with the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain whether 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Also, look for the bargain table close to the front with the store brimming with items as much as 50 percent off of the regular price. Insurance is confusing first of all, additionally it is constantly changing. An one that finds work within this profession can be considered a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to do work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that provides the doctors with scanned images that the latter will use as bases because of their diagnoses.
This online pharmacy is actually very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude won’t help the situation. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform lot more than provide prescriptions to patients.
It might be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at a number of financial institutions. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to your patient or customer. If you obtain prescriptions from month to month make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
Location and the type of employer include the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. I must add, I have never had virtually any emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. The application deadline is at late April, but it is best to apply much sooner.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse management of clients due for the perceived utilization of any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or a syringe. College pre-pharmacy study as little like a day or two which enable it to still pass the exam. If possible try to use the identical pharmacy as much as possible.
It is important to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives this kind of low wage which when doing work in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one receives a wage of $17 per hour minimum. Fear not, after a while you will know the best way to handle different forms of problems that comes about. They are also responsible for inspecting the operational treatments for dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
The live answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing in the first place, and it also is constantly changing. This is really a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions needless to say called qualifying life events or QLEs) before the next open enrollment season in November.
By giving your pharmacy the actual name of your medication you can better safe guard your health. The holding, the transfers, the new rules and also the mail-order requirements. Use those outlines as a roadmap to assist you study for that pharmacy tech certification test.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can obtain a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist around the counter. Drugs might be ordered by just entering the pharmacy website and placing an order using a click from the mouse button. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you should be looking out for as well because these names will proclaim these websites are safe for paying online.
While there is often a small chance you could get laid off (for instance, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you should not have much problem finding another job. ” A good reaction to this isn’t “I’m looking for a job. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn in pharmaceutical quality training will be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
#floxin
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can get a lot more done in the calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one along with the other country could be another, and also the avian temperature is the other. It is essential that the web doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. ” A good reply to this is not “I’m trying to find a job. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you ought to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim the websites are secure for paying online.
We were going on the big city to see a doctor, so it made sense. When all factors are believed, however, I would have to say that the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are quite comparable. In order to register using the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain sometimes a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
The answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing in the first place, plus it is constantly changing. An one that finds work on this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that delivers the doctors with scanned images how the latter make use of as bases because of their diagnoses.
It doesn’t seem fair folks don’t have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they are burdened with spending most of their life worrying about something that could affect their survival like this. The local temperature with the medicine producing country is one along with the other country might be another, and the avian temperature will be the other. Most drugs need to be stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to maintain the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Also, look for that bargain table close to the front of the store brimming with items around 50 percent from the regular price. The holding, the transfers, the newest rules along with the mail-order requirements. An individual who finds work on this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images that this latter use as bases because of their diagnoses.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can certainly be some times, you can have a lot more done in the calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country could be another, and the avian temperature will be the other. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe include the two names you ought to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim why these websites feel at ease for paying online.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due for the perceived utilization of any medical device, be it a pill or perhaps a syringe. College pre-pharmacy study as little being a day or two which enable it to still pass the exam. So as a buyer, you need to identify a traditional online pharmacy that’s licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered through your state. College pre-pharmacy study as little like a day or two and will still pass the exam. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better odds of being successful.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. The holding, the transfers, the new rules along with the mail-order requirements. Strong customer satisfaction skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of a pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must spend the money for entire cost out-of-pocket. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease in the shopping center that was about to be developed in the heart of Makati. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
An online pharmacy is quite a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart application on a secure server. An individual who finds work in this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images that this latter use as bases for diagnoses.
We were going towards the big city to determine a doctor, so it made sense. Factors staying taught in institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. It is very important that the online doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly provides medicine.
It doesn’t seem fair folks don’t have cheap drugs available to them for purchase and that they are burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one and also the other country might be another, and the avian temperature will be the other. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training is the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
We were going on the big city to view a doctor, so that it made sense. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, this is a fact. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you have to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim that these websites are secure for paying online.
While there is a small chance you could get laid off (for instance, if the chain supermarket closes some stores) you must not have much problem finding another job. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, this is a fact. In order to register with the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain whether 3 Level 3 qualifications.
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career being a PT mainly because it helps to make one more qualified once they apply for promotion. These are the pharmacist who works as a professor or lecture in a medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time within the other areas of pharmacy. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better probability of being successful.
Location and the sort of employer will be the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. Fear not, after a while you will know just how to handle different types of problems that may come about. You should find these records somewhere inside “Contact Us” section with the website.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude will not help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and invented exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can have a lot more done in the calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. Drugs can be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order with a click with the mouse button. It is very important that the internet doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
We were going to the big city to find out a doctor, so it made sense. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one and the other country could be another, and also the avian temperature could be the other. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you need to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim why these websites feel at ease for paying online.
Most patients were paying a high income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must give the entire cost out-of-pocket. As a smaller entrepreneur, just when was it time to increase prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
We were going towards the big city to view a doctor, so that it made sense. Factors staying taught in universities regularly variations, which is a fact. It is very important that the net doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly increases the medicine.
An online pharmacy is fairly a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing in the first place, and it also is constantly changing. The massive increase in people creating an online business for many of their shopping and daily needs has triggered many pharmacies having an online site built, where they feature numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to your neighborhood pharmacy.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart solution on a secure server. An individual who finds work on this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment providing you with the doctors with scanned images the latter use as bases for his or her diagnoses.
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of one’s medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart application on a secure server. An one that finds work on this profession can be considered a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to perform work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that delivers the doctors with scanned images how the latter uses as bases because of their diagnoses.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing which has a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech about it new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy understanding that it is really a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. They are also responsible for inspecting the operational control over dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to enhance the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
This online pharmacy is basically very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Ask the managers from the places in which you enjoy shopping if they offer these forms of programs, should you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Important point to be noticed is always that cost can’t be the first consideration. Use those outlines being a roadmap to help you study for that pharmacy tech certification test.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing first of all, and yes it is constantly changing. Strong customer support skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Most patients were paying a nice income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must spend the money for entire cost out-of-pocket. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are needed to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
In order to be eligible for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) has to be completed and aid is granted in relation to student need, tuition rates in the college, and other factors. I must add, I have never had just about any emotional disorder during my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which can be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
In order to qualify for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted in relation to student need, tuition rates on the college, and other factors. I must add, I have never had just about any emotional disorder in my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. The application deadline is at late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
In order to be entitled to federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted dependant on student need, tuition rates with the college, as well as other factors. The final volume of your certified local pharmacy professional study course takes a 12 month preparation software and also as soon because completing the particular tutorials you may purchase an associates education. If you get prescriptions from month to month make sure your pharmacy has your most current prescription insurance information.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing with a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. The last volume of a certified local pharmacy professional training program takes a one year preparation software and also as soon as the completing the actual tutorials you may purchase an associates education. You should find this info somewhere in the “Contact Us” section of the website.
To maximum benefit out of the card, use it every visit and keep track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. You may also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information to the computer.
Also, look for the bargain table near the front of the store full of items as much as 50 percent off the regular price. Insurance is confusing first of all, plus it is constantly changing. The massive rise in people using the internet for many of their shopping and everyday needs has led to many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they provide numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to your neighborhood pharmacy.
An online pharmacy is very a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Before taking any exams required by their state, they should pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Strong customer care skills certainly are a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, side effects, and other drug information. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and invented exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
We were going on the big city to see a doctor, in order that it made sense. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one and the other country could be another, as well as the avian temperature could be the other. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you should be looking out for as well because these names will proclaim why these websites feel at ease for paying online.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart software on a secure server. This is often a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions obviously called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due towards the perceived using any medical device, be it a pill or possibly a syringe. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two and may still pass the exam. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy just as much as possible.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. Fear not, as time passes you will know exactly how to handle different forms of problems that can come about. They are also in charge of inspecting the operational control over dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing first of all, plus it is constantly changing. An person that finds work within this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to do work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images that this latter make use of as bases for his or her diagnoses.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules and also the mail-order requirements. The massive rise in people online for many with their shopping and day to day needs has resulted in many pharmacies having an online site built, where they have numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due to the perceived use of any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or perhaps a syringe. The above image shows a secure protocol ( has used with the fraudster. There is basically no difference between ordering drugs from the drugstore in the United States than by having a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can get a lot more done in the calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. When all factors are viewed, however, I would need to say how the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. In order to register with all the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain the 3 Level 3 qualifications.
CVS Pharmacy must count on prescription drug sales to keep in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add an enormous markup to the prescription medications they sell. ” A good a reaction to this isn’t “I’m searching for a job. Most drugs need to get stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training will be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
By giving your pharmacy the actual name of your respective medication you can better safe guard your health. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart solution on a secure server. This is really a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are kept in (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart on a good server. Use those outlines as a roadmap to assist you study for that pharmacy tech certification test.
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career like a PT mainly because it helps for making one more qualified when they apply for promotion. These will be the pharmacist who works as being a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent with their time inside other areas of pharmacy. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. The holding, the transfers, the brand new rules as well as the mail-order requirements. Use those outlines as a roadmap to aid you study for your pharmacy tech certification test.
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career like a PT because it helps to make one more qualified after they apply for promotion. You might additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs available for purchase and that they are burdened with spending the rest of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, this is a fact. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
It is essential to note that does not every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage which when working in private pharmacies, it is most likely that one gets to be a wage of $17 per hour minimum. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a whole new policy understanding that it can be a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. They are also to blame for inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to further improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
It doesn’t seem fair folks don’t have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending the entire content of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. ” A good reply to this just isn’t “I’m searching for a job. In order to register with the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain sometimes a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must give the entire cost out-of-pocket. As a smaller entrepreneur, just when was it time to increase prices like Netflix. After you filled out the account, you’ll now go with a payment scheme.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a new policy which it is really a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these details somewhere within the “Contact Us” section with the website.
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot more than provide prescription medications to patients.
#clonazepam
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs available for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending most of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. ” A good response to this is just not “I’m looking for a job. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you should be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim these websites feel safe for paying online.
Most patients were paying a nice income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must give the entire cost out-of-pocket. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are needed to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and invented exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Location and the type of employer include the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. The last volume of a certified local pharmacy professional program takes a 12 month preparation software along with as soon since the completing the particular tutorials you may purchase an associates education. The application deadline is within late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that these are burdened with spending the entire content of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. ” A good reaction to this is just not “I’m searching for a job. It is extremely important that the internet doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly gives the medicine.
In order to be entitled to federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) have to be completed and aid is granted based on student need, tuition rates on the college, and also other factors. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. You should find these records somewhere within the “Contact Us” section in the website.
An online pharmacy is very a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart on a safe and secure server. Strong customer service skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Also, look for that bargain table close to the front of the store brimming with items approximately 50 percent off of the regular price. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart software on a secure server. Strong customer care skills certainly are a must when handling the hectic pace of a pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
An online pharmacy is pretty a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. Important point to become noticed is cost can’t often be the first consideration. Strong customer care skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered by your state. You might additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we have better odds of being successful.
While there is really a small chance you could get laid off (for example, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you must not have much problem finding another job. When all factors are believed, however, I would must say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. Make sure that you take some time to ask about a more affordable version so they will confirm the list.
This online pharmacy is basically very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or just being rude will not help the situation. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include supplying the precise measurements of oxygen or other kinds of gas concentrations inside patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
We were going for the big city to view a doctor, therefore it made sense. ” A good reply to this just isn’t “I’m looking for a job. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart on a good server. An individual that finds work with this profession can be considered a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that provides the doctors with scanned images how the latter use as bases for diagnoses.
To get the most out of the card, use it every visit and keep track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. These are the pharmacist who works as being a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of their time inside the other areas of pharmacy. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
To get the most out in the card, use it every visit whilst track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. You may also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better likelihood of being successful.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing using a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy which it is often a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria you need to include streptococci, which can be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered by your state. The above image shows a secure protocol ( has used from the fraudster. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy up to possible.
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatments for clients due towards the perceived use of any medical device, be it a pill or even a syringe. You might also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. They also can check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
We were going for the big city to see a doctor, so that it made sense. ” A good response to this is just not “I’m seeking a job. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you ought to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim these websites feel safe for paying online.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to your patient or customer. The application deadline is late April, however it is best to apply much sooner.
It may be used by fraudsters to gain access to your accounts at a variety of financial institutions. When I asked the tech concerning this new action she stated that yes, it is a whole new policy understanding that it is a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and can include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Ask the managers with the places in places you enjoy shopping if they feature these kinds of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot over provide prescription medications to patients.
Location and the form of employer are the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy understanding that it is really a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. If you receive prescriptions every month make sure your pharmacy has your most up to date prescription insurance information.
Also, look for the bargain table near the front in the store filled with items as much as 50 percent off the regular price. Insurance is confusing first of all, additionally it is constantly changing. Use those outlines as a roadmap to aid you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
While there is often a small chance you can get laid off (as an example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you shouldn’t have much problem finding another job. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one along with the other country may be another, and the avian temperature could be the other. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you ought to be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim that these websites feel safe for paying online.
#phentermine
We were going towards the big city to find out a doctor, so it made sense. ” A good response to this is just not “I’m seeking a job. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to hold the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Most patients were paying big money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they’d not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay for the entire cost out-of-pocket. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude won’t help the situation. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include providing the precise measurements of oxygen or other forms of gas concentrations inside the patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Also, look for the bargain table near the front with the store packed with items as much as 50 percent from the regular price. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English like a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. An individual that finds work with this profession can be described as a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to perform work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images how the latter make use of as bases for their diagnoses.
While there can be a small chance you have access to laid off (by way of example, if the chain supermarket closes some stores) you mustn’t have much problem finding another job. ” A good reaction to this isn’t “I’m searching for a job. In order to register using the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain the 3 Level 3 qualifications.
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease inside the shopping center that’s about being developed inside the heart of Makati. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
It is important to note that not every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage and that when employed in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one turns into a wage of $17 hourly minimum. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy understanding that it is a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. The application deadline is at late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
It may be used by fraudsters to gain access to your accounts at a variety of financial institutions. The final volume of the certified local pharmacy professional training program takes a 12 month preparation software and also as soon as the completing the specific tutorials you might purchase an associates education. You should find these details somewhere in the “Contact Us” section with the website.
If you might be disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally will surely have your student loans discharged. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other kinds of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood along with measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing with a write-up that contained just a bit of Schadenfreude. Fear not, after a while you will know exactly how to handle different kinds of problems that may come about. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational management of dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to boost the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
An online pharmacy is pretty a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. Important point being noticed is always that cost can’t often be the first consideration. The massive increase in people online for many of these shopping and daily needs has resulted in many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they provide numerous services which can help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your neighborhood pharmacy.
We were going towards the big city to find out a doctor, in order that it made sense. When all factors are viewed, however, I would must say that this prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you have to be looking out for as well since these names will proclaim why these websites are safe for paying online.
Location and the form of employer are the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. When I asked the tech concerning this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy which it is really a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. They are also responsible for inspecting the operational treatments for dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to enhance the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
This online pharmacy is actually very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Ask the managers in the places where you enjoy shopping if they offer these forms of programs, should you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other kinds of gas concentrations inside patient’s blood as well as measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
If you might be disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you definitely generally can have your student loans discharged. Ask the managers from the places in places you enjoy shopping if they provide these varieties of programs, in the event you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other kinds of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood as well as measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
It is vital to note that every pharmacy technician receives this kind of low wage which when in private pharmacies, it is most likely that one gets to be a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed by way of a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. The application deadline is within late April, however it is best to apply much sooner.
An online pharmacy is very a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. The holding, the transfers, the newest rules and the mail-order requirements. Use those outlines as being a roadmap to help you you study to the pharmacy tech certification test.
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, or another drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease in the shopping center which was about to be developed inside the heart of Makati. After you done the account, you are going to now select a payment scheme.
By giving your pharmacy the complete name of your respective medication you’ll be able to better safe guard your health. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart on a good server. This is a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions needless to say called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, side effects, or other drug information. Ask the managers of the places in places you enjoy shopping if they feature these types of programs, should you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The moon sheds her subtle influence on all of the, adding for the variables. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two and can still pass the exam. There is really no difference between ordering drugs from the drugstore inside United States than by way of a Canada pharmacy except to the price.
It could be used by fraudsters gain access to your accounts at numerous financial institutions. I must add, I have never had virtually any emotional disorder during my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which can be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart application on a safe and secure server. The massive increase in people online for many of these shopping and day by day needs has resulted in many pharmacies having an online site built, where they feature numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
This online pharmacy is really very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Ask the managers from the places where you enjoy shopping if they feature these forms of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due to the perceived utilization of any medical device, it could be a pill or perhaps a syringe. The above image shows a secure protocol ( will be used from the fraudster. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we now have better probability of being successful.
While there is a small chance you could get laid off (by way of example, if the chain supermarket closes some stores) you shouldn’t have much problem finding another job. The local temperature with the medicine producing country is one as well as the other country may be another, and also the avian temperature will be the other. Make sure you take the time to ask about a more affordable version in order that they will look into the list.
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career as being a PT mainly because it helps in making one more qualified when they apply for promotion. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( has been used through the fraudster. There is actually no difference between ordering drugs coming from a drugstore inside United States than by way of a Canada pharmacy except for your price.
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career like a PT since it helps to make one more qualified when they apply for promotion. To find degree programs that train you for any career as being a pharmacy technician, you can check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we have better probability of being successful.
The certification does play a huge role in making a rewarding career as a PT as it helps in making one more qualified whenever they apply for promotion. To find degree programs that train you for the career as a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. So like a buyer, you’ll need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that’s licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
It is important to note that every pharmacy technician receives a real low wage which when doing work in private pharmacies, it is most likely that one receives a wage of $17 per hour minimum. I must add, I have never had just about any emotional disorder within my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. If you obtain prescriptions every month make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) have to be completed and aid is granted in relation to student need, tuition rates on the college, as well as other factors. The very last volume of the certified local pharmacy professional program takes a 12 month preparation software as well as as soon since the completing the particular tutorials you could purchase an associates education. You should find these details somewhere within the “Contact Us” section in the website.
Online pharmacy for skin treatments
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. After you filled out the account, you may now select a payment scheme.
#toprol
buy facebook account website for selling accounts accounts for sale
It doesn’t seem fair individuals don’t have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something that could affect their survival like this. When all factors are considered, however, I would ought to say how the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy can be comparable. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you ought to be looking out for as well because these names will proclaim the websites feel at ease for paying online.
Buy antibiotics online
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can have a lot more done in a calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Drugs may be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order with a click from the mouse button. In order to register with the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain whether 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Order anxiety medication online
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, and other drug information. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude will not help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and invented exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Metformin prescription refill online
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. As a smaller entrepreneur, just when was it time to boost prices like Netflix. After you done the account, you will now go with a payment scheme.
Online pharmacy for Lisinopril
There are two ways to become a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered by your state. You may additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So as a buyer, you may need to identify a traditional online pharmacy which is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Online pharmacy safety tips
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they’d not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay for the entire cost out-of-pocket. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que space to lease within the shopping center that has been about being developed in the heart of Makati. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Gabapentin online consultation
We were going on the big city to see a doctor, so that it made sense. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one and also the other country might be another, along with the avian temperature will be the other. Most drugs need to be stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training may be the necessary steps to hold the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Online pharmacy for Lisinopril
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due for the perceived using any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or possibly a syringe. College pre-pharmacy study as little as being a day or two which enable it to still pass the exam. So as being a buyer, you will need to identify an authentic online pharmacy which is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Order anti-inflammatory medications online
While there is really a small chance you could get laid off (as an example, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you must not have much problem finding another job. When all factors are believed, however, I would ought to say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. It is essential that the net doctor exactly understands exactly what the problem is and accordingly gives the medicine.
Prescription eye care products online
While there is often a small chance you can get laid off (as an example, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you shouldn’t have much problem finding another job. Drugs could be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order which has a click of the mouse button. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one from the things pharmacists learn in pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Pharmacy site
This online pharmacy is actually very great for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a small entrepreneur, when is it time to raise prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Online pharmacy for sleep aids
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career being a PT because it helps to produce one more qualified when they apply for promotion. To find degree programs that train you for the career like a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information to the computer.
Buy cholesterol medication online
It is essential to note that not every pharmacy technician receives this kind of low wage understanding that when in private pharmacies, it is most likely that one receives a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. The pharmacist technician will need to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational management of dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to boost the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Simvastatin online drugstore
buy facebook account account marketplace accounts market
It is important to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives a real low wage and that when in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one gets to be a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. I must add, I have never had virtually any emotional disorder within my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. If you receive prescriptions from month to month make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
Buy Lipitor online
This online pharmacy is basically very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Online drugstore
While there is often a small chance you can get laid off (by way of example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you shouldn’t have much problem finding another job. Drugs can be ordered by simply entering the pharmacy website and placing an order which has a click from the mouse button. It is crucial that the internet doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly provides medicine.
Losartan mail-order pharmacy
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can have a lot more done in the calm friendly manner then you ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. Factors staying taught in institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. In order to register while using GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain either a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Simvastatin online drugstore
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing to begin with, plus it is constantly changing. An individual that finds work within this profession can be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to execute work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment that gives the doctors with scanned images how the latter make use of as bases for his or her diagnoses.
Online drugstore
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or another drug information. Ask the managers from the places in which you enjoy shopping if they provide these kinds of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Prescription transfer online
Pharmacy technicians also usually do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or another drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease inside shopping center that has been about being developed inside heart of Makati. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Pharmacy site
This online pharmacy is absolutely very great for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Ask the managers from the places where you enjoy shopping if they offer these varieties of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. After you filled out the account, you will now go with a payment scheme.
Online pharmacy for pet medications
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatments for clients due on the perceived utilization of any medical device, it could be a pill or even a syringe. These include the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in almost any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time within the other areas of pharmacy. There is absolutely no difference between ordering drugs coming from a drugstore in the United States than through a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
Online prescription refill
We were going towards the big city to find out a doctor, so that it made sense. ” A good reaction to this is just not “I’m seeking a job. It is extremely important that the net doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
Affordable medications online
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or another drug information. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude won’t help the situation. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include supplying the precise measurements of oxygen or other types of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Metformin prescription refill online
If you might be disabled according to federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you generally will surely have your student loans discharged. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease in the shopping center that’s about to become developed in the heart of Makati. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include providing the precise measurements of oxygen or other forms of gas concentrations inside patient’s blood along with measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Online pharmacy coupons
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that these are burdened with spending the entire content of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. When all factors are believed, however, I would have to say that the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. It is essential that the web doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly gives the medicine.
Online pharmacy for heart medications
It is vital to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives this type of low wage knowning that when employed in private pharmacies, it is almost certainly that one turns into a wage of $17 per hour minimum. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy understanding that it is a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. The application deadline is late April, but it’s best to apply much sooner.
Online pharmacy FAQs
If you happen to be disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally will surely have your student loans discharged. Ask the managers from the places that you enjoy shopping if they have these varieties of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Order anxiety medication online
In order to be entitled to federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted based on student need, tuition rates on the college, and also other factors. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a new policy knowning that it is really a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. The application deadline is at late April, however it is best to apply much sooner.
Order anxiety medication online
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse management of clients due for the perceived utilization of any medical device, whether it’s a pill or perhaps a syringe. These would be the pharmacist who works as being a professor or lecture in a medical college; they spend around 50 per cent with their time inside the other areas of pharmacy. There is really no difference between ordering drugs from your drugstore inside the United States than by having a Canada pharmacy except to the price.
Online pharmacy for pet medications
CVS Pharmacy must depend upon prescription drug sales to stay in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t have to add a massive markup to the prescribed drugs they sell. When all factors are thought, however, I would must say that this prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. Most drugs need to get stored at exact temperatures, so one with the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training could be the necessary steps to hold the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Online pharmacy for sleep aids
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they have to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. The massive boost in people creating an online business for many of their shopping and day to day needs has resulted in many pharmacies having an online site built, where they have numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to any local pharmacy.
Online pharmacy for chronic conditions
An online pharmacy is quite a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. Insurance is confusing first of all, and yes it is constantly changing. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a brand new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions obviously called qualifying life events or QLEs) before next open enrollment season in November.
Prescription eye care products online
To obtain the most out with the card, use it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. The above image shows a secure protocol ( has used through the fraudster. They can also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in to the computer.
Online pharmacy loyalty program
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) must be completed and aid is granted dependant on student need, tuition rates with the college, and other factors. The pharmacist technician have to have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to a patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, which are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Online pharmacy for mental health
There are two ways for being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered through your state. You might additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So as a buyer, you may need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Online pharmacy for travel medications
The moon sheds her subtle influence on all on this, adding for the variables. You may additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. If possible try to use exactly the same pharmacy around possible.
Order anti-inflammatory medications online
It can be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at many different financial institutions. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy knowning that it is often a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria you need to include streptococci, that happen to be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that happen to be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Online pharmacy for chronic conditions
It may be used by fraudsters to get into your accounts at a variety of financial institutions. When I asked the tech concerning this new action she stated that yes, it is a brand new policy understanding that it is really a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. You should find this info somewhere inside “Contact Us” section in the website.
Safe online pharmacy
The moon sheds her subtle relation to all of the, adding to the variables. To find degree programs that train you for any career as being a pharmacy technician, you are able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. They could also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information to the computer.
Buy cholesterol medication online
We were going for the big city to view a doctor, so that it made sense. Drugs may be ordered by simply entering the pharmacy website and placing an order using a click from the mouse button. It is essential that the net doctor exactly understands what are the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
Buy erectile dysfunction medication online
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart on a good server. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are stuck (with minor exceptions obviously called qualifying life events or QLEs) before the next open enrollment season in November.
Order anti-inflammatory medications online
Location and the form of employer are the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. Fear not, with time you will know just how to handle different kinds of problems that will come about. The application deadline is late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
#furosemide
To obtain the most out with the card, apply it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. These will be the pharmacist who works as a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent with their time in the other areas of pharmacy. They also can check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information into the computer.
Online pharmacy for sleep aids
It doesn’t seem fair folks don’t have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something that could affect their survival like this. When all factors are considered, however, I would must say that the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy can be comparable. Make sure you take some time to ask about a more affordable version so they really will check the list.
Online pharmacy loyalty program
Most patients were paying a high income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay for the entire cost out-of-pocket. Ask the managers with the places in places you enjoy shopping if they feature these varieties of programs, should you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. After you filled out the account, you are going to now decide on a payment scheme.
Metformin prescription refill online
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Before taking any exams necessary for their state, they must pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. An one that finds work in this profession can be described as a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment providing you with the doctors with scanned images how the latter uses as bases for his or her diagnoses.
Online pharmacy for Lisinopril
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career as a PT since it helps to produce one more qualified when they apply for promotion. To find degree programs that train you for any career like a pharmacy technician, you are able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we now have better odds of being successful.
Health and wellness products online
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or another drug information. Ask the managers in the places in which you enjoy shopping if they feature these kinds of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. After you done the account, you are going to now select a payment scheme.
Buy antiviral medications online
In order to be eligible for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) should be completed and aid is granted based on student need, tuition rates with the college, and other factors. The last volume of an certified local pharmacy professional training course takes a 12 month preparation software as well as as soon because completing the actual tutorials you may purchase an associates education. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational treating dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to further improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Mail-order pharmacy
By giving your pharmacy the actual name of your medication you are able to better safe guard your health. Before taking any exams required by their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English like a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Strong customer support skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Secure online pharmacy
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that they may be burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something which could affect their survival like this. When all factors are believed, however, I would must say that the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you ought to be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim these websites are secure for paying online.
Prescription eye care products online
This online pharmacy is basically very ideal for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot a lot more than provide prescription medications to patients.
Prescription allergy medications online
This online pharmacy is basically very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease inside the shopping center that’s about to be developed in the heart of Makati. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists perform a lot a lot more than provide prescription drugs to patients.
Gabapentin online consultation
It could be used by fraudsters gain access to your accounts at numerous financial institutions. The pharmacist technician will need to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to a patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria you need to include streptococci, that happen to be chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, which can be clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Albuterol online
The pharmaceutical industry especially do not want to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due towards the perceived utilization of any medical device, whether it’s a pill or a syringe. To find degree programs that train you for a career as being a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we now have better probability of being successful.
Online pharmacy for skin treatments
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing which has a write-up that contained just a bit of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy understanding that it is often a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. You should find this info somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section with the website.
Online pharmacy for Lisinopril
We were going to the big city to view a doctor, so that it made sense. Factors staying taught in universities regularly variations, that’s a fact. Make certain that you take the time to ask about a more affordable version so they really will check the list.
Online prescription refill
By giving your pharmacy the precise name of one’s medication you are able to better safe guard your health. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart on a good server. Use those outlines like a roadmap to help you you study for your pharmacy tech certification test.
Online pharmacy for pet medications
While there can be a small chance you can get laid off (for example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you shouldn’t have much problem finding another job. ” A good response to this isn’t “I’m seeking a job. Most drugs need to get stored at exact temperatures, so one from the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training may be the necessary steps to keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Online pharmacy for sleep aids
This online pharmacy is really very helpful for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude can’t help the situation. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Online pharmacy
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Insurance is confusing in the first place, and it also is constantly changing. An one that finds work on this profession can certainly be a radiology technician if his competency qualifies him to complete work using x-ray, ultra-sound, CAT or ECG equipment providing you with the doctors with scanned images the latter use as bases because of their diagnoses.
Online pharmacy for diabetes medications
CVS Pharmacy must depend upon prescription drug sales to keep in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t must add a tremendous markup to the medications they sell. When all factors are believed, however, I would need to say that the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. It is essential that the web doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly provides the medicine.
Online health products
Location and the type of employer are the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order with a patient or customer. The application deadline is within late April, but it’s best to apply much sooner.
#medrol
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Ask the managers with the places that you enjoy shopping if they provide these kinds of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. After you done the account, you are going to now select a payment scheme.
Prescription eye care products online
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Insurance is confusing in the first place, and it also is constantly changing. Use those outlines as a roadmap to assist you study for that pharmacy tech certification test.
Prescription eye care products online
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted effects, or any other drug information. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a space to lease within the shopping center that’s about being developed inside heart of Makati. After you filled in the account, you may now go with a payment scheme.
Online pharmacy coupons
If you happen to be disabled in accordance with federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you certainly generally may have your student loans discharged. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease inside the shopping center which was about to be developed within the heart of Makati. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Secure online pharmacy
Location and the form of employer are the final factors in determining simply how much pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to some patient or customer. The application deadline is at late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
Buy antibiotics online
It is important to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage understanding that when in private pharmacies, it is more than likely that one turns into a wage of $17 each hour minimum. The final volume of the certified local pharmacy professional study course takes a twelve month preparation software in addition to as soon because completing the actual tutorials you could purchase an associates education. They are also in charge of inspecting the operational treatments for dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to enhance the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Online health products
An online pharmacy is very a help in a embarrassing scenario like this. Important point to be noticed is cost can’t always be the first consideration. Strong customer service skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of a pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Buy Lipitor online
The call center company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Before taking any exams necessary for their state, they have to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Use those outlines being a roadmap to assist you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Online pharmacy for sleep aids
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can certainly be some times, you can have a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. Make sure you take enough time to ask about a less expensive version so they really will look into the list.
Order anxiety medication online
Location and the form of employer will be the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. Fear not, as time passes you will know precisely how to handle different varieties of problems that comes about. If you get prescriptions from month to month make sure your pharmacy has your most current prescription insurance information.
Amoxicillin delivery service
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained just a bit of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy and that it is a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. The application deadline is in late April, but it is best to apply much sooner.
Buy antiviral medications online
The moon sheds her subtle impact on all on this, adding on the variables. To find degree programs that train you to get a career as being a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. There is really no difference between ordering drugs from your drugstore within the United States than by having a Canada pharmacy except for your price.
Prescription weight loss pills online
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude will not help the situation. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include providing the precise measurements of oxygen or other varieties of gas concentrations in the patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Secure online pharmacy
There are two ways for being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. You might also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. If possible try to use a similar pharmacy as much as possible.
Online pharmacy for hormone therapy
By giving your pharmacy the actual name of the medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules as well as the mail-order requirements. Strong customer service skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of the pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Albuterol online
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( will be used from the fraudster. There is basically no difference between ordering drugs coming from a drugstore inside the United States than by having a Canada pharmacy except for the price.
Online pharmacy for hormone therapy
To make the most out with the card, put it to use every visit whilst track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. To find degree programs that train you for the career as a pharmacy technician, you are able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. So as a buyer, you will need to identify a realistic online pharmacy which is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Online pharmacy reviews
By giving your pharmacy the actual name of one’s medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules and also the mail-order requirements. Use those outlines being a roadmap to aid you study for that pharmacy tech certification test.
Online pharmacy for hormone therapy
In order to qualify for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) should be completed and aid is granted dependant on student need, tuition rates at the college, and other factors. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a new policy which it is a “law” that all pharmacies must adhere to. The application deadline is late April, however it is best to apply much sooner.
Buy vitamins and supplements online
The certification does play a huge role in making a rewarding career as a PT mainly because it helps to make one more qualified whenever they apply for promotion. The above image shows that the secure protocol ( has been used from the fraudster. If possible try to use the identical pharmacy up to possible.
Safe online pharmacy
An online pharmacy is quite a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. The holding, the transfers, the new rules along with the mail-order requirements. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a fresh year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are stuck (with minor exceptions of course called qualifying life events or QLEs) prior to the next open enrollment season in November.
Buy antibiotics online
Location and the kind of employer include the final factors in determining simply how much pharmacists make. The pharmacist technician have to have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to your patient or customer. They are also to blame for inspecting the operational control over dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Pharmacy app
If you’re disabled based on federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally will surely have your student loans discharged. Ask the managers from the places where you enjoy shopping if they offer these varieties of programs, if you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other types of gas concentrations inside patient’s blood and also measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Health and wellness products online
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, side effects, or any other drug information. Ask the managers with the places in which you enjoy shopping if they feature these kinds of programs, in the event you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Generic medications online
This online pharmacy is actually very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude will not help the situation. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other varieties of gas concentrations inside patient’s blood along with measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Losartan mail-order pharmacy
If you happen to be disabled in accordance with federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally might have your student loans discharged. As a tiny entrepreneur, when was it time to boost prices like Netflix. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Online pharmacy for Lisinopril
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career as a PT as it helps for making one more qualified when they apply for promotion. To find degree programs that train you for the career as a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve better likelihood of being successful.
Online pharmacy for skin treatments
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing with a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. When I asked the tech concerning this new action she stated that yes, it is a whole new policy and that it is really a “law” that every pharmacies must adhere to. The application deadline is at late April, but it is best to apply much sooner.
Online pharmacy for contraceptives
It is important to note that does not every pharmacy technician receives such a low wage which when employed in private pharmacies, it is almost certainly that one receives a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. I must add, I have never had any kind of emotional disorder inside my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational management of dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Online pharmacy for mental health
The answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart on a safe and secure server. Strong customer service skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Order anxiety medication online
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Insurance is confusing in the first place, additionally it is constantly changing. Strong customer support skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of a pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Gabapentin online consultation
CVS Pharmacy must rely on prescription drug sales to keep in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add an enormous markup to the medications they sell. When all factors are believed, however, I would need to say that the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are quite comparable. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe include the two names you have to be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim the websites feel at ease for paying online.
#sominex
The certification does play a huge role in making a rewarding career like a PT since it helps to make one more qualified after they apply for promotion. These include the pharmacist who works as being a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of the time within the other areas of pharmacy. So like a buyer, you’ll need to identify an authentic online pharmacy which is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Albuterol online
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it might be some times, you can have a lot more done in a calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist around the counter. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe include the two names you should be looking out for as well since these names will proclaim that these websites feel at ease for paying online.
Pharmacy app
To obtain the most out with the card, use it every visit and track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. You may additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So as being a buyer, you may need to identify a realistic online pharmacy that is certainly licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Mail-order pharmacy
Most patients were paying good money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must spend the money for entire cost out-of-pocket. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que an area to lease in the shopping center that was about to get developed within the heart of Makati. After you done the account, you are going to now decide on a payment scheme.
Pharmacy app
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs at hand for purchase and that these are burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. When all factors are believed, however, I would must say how the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are quite comparable. Make sure you take enough time to ask about a more affordable version in order that they will confirm the list.
Online pharmacy loyalty program
Pharmacy technicians also do not provide advice to patients about medication options, negative effects, or any other drug information. As a little entrepreneur, when was it time to improve prices like Netflix. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other varieties of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood in addition to measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Order anxiety medication online
An online pharmacy is very a help in the embarrassing scenario like this. Before taking any exams required by their state, they must pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English as being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. The massive surge in people using the web for many of these shopping and daily needs has resulted in many pharmacies having an online site built, where they provide numerous services which will help you avoid making unnecessary trips to the local pharmacy.
Online pharmacy consultation
The pharmaceutical industry especially do not want to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse management of clients due for the perceived use of any medical device, it could be a pill or a syringe. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( will be used with the fraudster. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we now have better odds of being successful.
Online pharmacy consultation
It doesn’t seem fair people don’t have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending most of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. Factors staying taught in educational institutions regularly variations, that’s a fact. Most drugs need being stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training will be the necessary steps to maintain the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Buy antibiotics online
If you are disabled in accordance with federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, you then generally may have your student loans discharged. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude will not help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Order anxiety medication online
The moon sheds her subtle influence on all with this, adding on the variables. To find degree programs that train you for a career being a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve got better chances of being successful.
Prescription eye care products online
In order to be entitled to federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) have to be completed and aid is granted based upon student need, tuition rates in the college, along with other factors. When I asked the tech about it new action she stated that yes, it is a new policy and that it is often a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these details somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section from the website.
Online pharmacy for skin treatments
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing with a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. Fear not, with time you will know exactly how to handle different types of problems that can come about. You should find this info somewhere inside the “Contact Us” section from the website.
Online prescription refill
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que space to lease inside the shopping center that has been about to get developed inside the heart of Makati. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Online pharmacy for Lisinopril
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can get yourself a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist about the counter. Drugs may be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order which has a click from the mouse button. It is very important that the web doctor exactly understands just what the problem is and accordingly gives the medicine.
Online pharmacy for heart medications
Also, look for the bargain table near the front from the store filled with items around 50 percent off of the regular price. Important point to get noticed is the fact that cost can’t often be the first consideration. This can be a common occurrence as January 1 kicks off a whole new year of pharmacy benefits and beneficiaries are locked in (with minor exceptions naturally called qualifying life events or QLEs) until the next open enrollment season in November.
Order Amlodipine from an online pharmacy
If you’re disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you definitely generally might have your student loans discharged. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. After you filled in the account, you’ll now select a payment scheme.
Prescription eye care products online
There are two ways to get a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered by your state. You might additionally check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. So being a buyer, you’ll need to identify a geniune online pharmacy that is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Secure online pharmacy
If you’re disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you generally might have your student loans discharged. As a smaller entrepreneur, when was it time to raise prices like Netflix. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include supplying the precise measurements of oxygen or other forms of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood as well as measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Online pharmacy coupons
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams essental to their state, they have to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Strong customer service skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of your pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Prescription allergy medications online
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. Fear not, after a while you will know the best way to handle different types of problems that may come about. The application deadline is within late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
Online pharmacy with fast shipping
An online pharmacy is pretty a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. The holding, the transfers, the brand new rules as well as the mail-order requirements. The massive increase in people using the web for many of their shopping and day to day needs has triggered many pharmacies having an internet site built, where they offer numerous services which can help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your neighborhood pharmacy.
Online pharmacy
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due on the perceived use of any medical device, be it a pill or perhaps a syringe. To find degree programs that train you for any career as being a pharmacy technician, it is possible to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we’ve got better odds of being successful.
Online pharmacy consultation
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained just a little of Schadenfreude. Fear not, with time you will know the best way to handle different varieties of problems that can come about. The application deadline is within late April, yet it’s best to apply much sooner.
#benoquin
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart on a good server. The massive surge in people using the web for many with their shopping and day by day needs has generated many pharmacies having a website built, where they have numerous services which may help you avoid making unnecessary trips to the local pharmacy.
Online pharmacy
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams required by their state, they must pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. The massive surge in people creating an online business for many with their shopping and daily needs has generated many pharmacies having a web site built, where they have numerous services which may help you avoid making unnecessary trips to the local pharmacy.
Online pharmacy for hormone therapy
An online pharmacy is very a help in an embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable web business puts their shopping cart on a good server. Use those outlines like a roadmap to assist you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Secure online pharmacy
It is very important to note that does not every pharmacy technician receives a real low wage and that when doing work in private pharmacies, it is almost certainly that one turns into a wage of $17 by the hour minimum. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed by a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to a patient or customer. They are also to blame for inspecting the operational control over dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to further improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Online pharmacy for mental health
Location and the sort of employer include the final factors in determining the amount pharmacists make. The last volume of an certified local pharmacy professional training program takes a twelve month preparation software and also as soon as the completing the actual tutorials you may purchase an associates education. If you will get prescriptions from month to month make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
Online pharmacy consultation
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of your medication you are able to better safe guard your health. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules and the mail-order requirements. Strong customer support skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Online pharmacy for sleep aids
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Before taking any exams required by their state, they should pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. The massive increase in people creating an online business for many of the shopping and everyday needs has led to many pharmacies having a website built, where they feature numerous services which can assist you avoid making unnecessary trips to your neighborhood pharmacy.
Buy antiviral medications online
Most patients were paying big money for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay for the entire cost out-of-pocket. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or being rude can’t help the situation. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include supplying the precise measurements of oxygen or other kinds of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood as well as measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Online pharmacy for skin treatments
CVS Pharmacy must rely on prescription drug sales to stay in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t must add a massive markup to the prescribed drugs they sell. Factors staying taught in educational facilities regularly variations, that’s a fact. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn within pharmaceutical quality training will be the necessary steps to maintain the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Pharmacy delivery service
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a space to lease in the shopping center which was about to get developed within the heart of Makati. After you completed the account, you are going to now select a payment scheme.
#lopid
Most patients were paying a nice income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay the entire cost out-of-pocket. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are necessary to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. Instead, I simply copied the hyperlink and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Online pharmacy
This online pharmacy is basically very of great help for old ailing patients and physically disabled persons. As a tiny entrepreneur, when was it time to increase prices like Netflix. According towards the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot over provide prescription medications to patients.
Online pharmacy
Most patients were paying a nice income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay for the entire cost out-of-pocket. Ask the managers of the places where you enjoy shopping if they have these varieties of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include providing the precise measurements of oxygen or other forms of gas concentrations within the patient’s blood as well as measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Prescription drugs online
The certification does play an important role in making a rewarding career like a PT mainly because it helps to make one more qualified once they apply for promotion. You might also check out “Physician Assistant Is a Top Healthcare Career. There is absolutely no difference between ordering drugs from the drugstore inside United States than via a Canada pharmacy except to the price.
Online pharmacy
Location and the type of employer include the final factors in determining just how much pharmacists make. When I asked the tech relating to this new action she stated that yes, it is a whole new policy and that it can be a “law” that most pharmacies must adhere to. You should find these records somewhere within the “Contact Us” section from the website.
Online prescription refill
An online pharmacy is pretty a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Important point to be noticed is cost can’t always be the first consideration. Strong customer service skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Prescription eye care products online
An online pharmacy is quite a help within an embarrassing scenario like this. Any reputable business online puts their shopping cart application on a secure server. Strong customer satisfaction skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of your pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Online pharmacy with fast shipping
Woah! I’m really enjoying the template/theme of this blog.
It’s simple, yet effective. A lot of times it’s very hard to get that “perfect balance” between usability and visual appeal.
I must say you’ve done a fantastic job with
this. In addition, the blog loads super quick for me on Internet explorer.
Excellent Blog! https://tinyurl.com/28555853 gamefly 3 month free trial
By giving your pharmacy the precise name of your medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Any reputable online business puts their shopping cart software on a good server. Use those outlines as a roadmap to help you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Mail-order pharmacy
By giving your pharmacy the exact name of your medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Important point to get noticed is always that cost can’t be the first consideration. The massive rise in people online for many of these shopping and day by day needs has resulted in many pharmacies having a web site built, where they have numerous services which may help you avoid making unnecessary trips to your local pharmacy.
Buy cholesterol medication online
In order to be eligible for a federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) should be completed and aid is granted based upon student need, tuition rates on the college, as well as other factors. The pharmacist technician must have the prepared prescription, reviewed by the pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to a patient or customer. You should find this info somewhere within the “Contact Us” section from the website.
Buy Lipitor online
The live answering services company company later changed its name to e – Telecare Global Soltions in 2004. Important point to be noticed is always that cost can’t always be the first consideration. Use those outlines as a roadmap to help you study to the pharmacy tech certification test.
Online pharmacy for Lisinopril
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can get yourself a lot more done in the calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist on the counter. ” A good reply to this is just not “I’m looking for a job. Make sure that you take some time to ask about a less expensive version so they will look into the list.
#levothroid
CVS Pharmacy must rely on prescription drug sales to stay in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add an enormous markup to the prescription drugs they sell. Drugs might be ordered by only entering the pharmacy website and placing an order with a click from the mouse button. It is essential that the internet doctor exactly understands what the problem is and accordingly gives the medicine.
Prescription weight loss pills online
It doesn’t seem fair people don’t have cheap drugs available for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending the remainder of their life worrying about a thing that could affect their survival like this. When all factors are believed, however, I would must say the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy are very comparable. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe would be the two names you have to be looking out for as well since these names will proclaim why these websites are secure for paying online.
Losartan mail-order pharmacy
There are two ways for being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered by your state. To find degree programs that train you to get a career as a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. They may also check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
Online pharmacy safety tips
To obtain the most out of the card, utilize it every visit and make track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. These would be the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of their time in the other areas of pharmacy. So like a buyer, you will need to identify a traditional online pharmacy that is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Online pharmacy FAQs
We were going towards the big city to view a doctor, so that it made sense. When all factors are viewed, however, I would have to say that this prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy can be comparable. In order to register with all the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain either a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Prescription weight loss pills online
Most physiologists required a Ph – D degree and licensing. Any reputable internet business puts their shopping cart software on a good server. Use those outlines as being a roadmap to help you you study for the pharmacy tech certification test.
Pharmacy app
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it can be some times, you can have a lot more done in the calm friendly manner then you ever will accomplish by pounding your fist around the counter. The local temperature in the medicine producing country is one along with the other country might be another, as well as the avian temperature will be the other. Make certain you take time to ask about a more affordable version so they really will look into the list.
Online pharmacy safety tips
In order to qualify for federal loans a Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA) should be completed and aid is granted in relation to student need, tuition rates with the college, and also other factors. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed with a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to your patient or customer. Cocci are sphere-shaped bacteria and will include streptococci, that are chains of cocci bacteria, and staphylococci, that are clusters of cocci bacteria1.
Metformin prescription refill online
There are two ways for being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered from your state. These would be the pharmacist who works like a professor or lecture in different medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of these time inside other areas of pharmacy. So as being a buyer, you may need to identify an authentic online pharmacy that’s licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Prescription weight loss pills online
It is very important to note that doesn’t every pharmacy technician receives this kind of low wage which when employed in private pharmacies, it is probably that one receives a wage of $17 each hour minimum. The final volume of the certified local pharmacy professional training course takes a 12 month preparation software and also as soon since the completing the particular tutorials you might purchase an associates education. They are also accountable for inspecting the operational treatments for dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to boost the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Prescription drugs online
While there can be a small chance you could get laid off (for example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you mustn’t have much problem finding another job. Factors staying taught in institutions regularly variations, what a fact. Make sure that you take some time to ask about a cheaper version so they really will confirm the list.
Simvastatin online drugstore
If you are disabled based on federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you definitely generally may have your student loans discharged. As a small entrepreneur, when is it time to improve prices like Netflix. After you filled out the account, you will now decide on a payment scheme.
Buy antidepressants online
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can have a lot more done in a very calm friendly manner you then ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Drugs may be ordered by simply entering the pharmacy website and placing an order which has a click of the mouse button. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one of the things pharmacists learn included in pharmaceutical quality training will be the necessary steps to help keep the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Buy erectile dysfunction medication online
It is essential to note that not every pharmacy technician receives a real low wage knowning that when employed in private pharmacies, it is probably that one receives a wage of $17 per hour minimum. When I asked the tech about this new action she stated that yes, it is a fresh policy which it is really a “law” that pharmacies must adhere to. They are also to blame for inspecting the operational treatments for dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Online pharmacy for pet medications
Most patients were paying a nice income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must give the entire cost out-of-pocket. Ask the managers with the places in which you enjoy shopping if they provide these kinds of programs, in the event you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
#frumil
It can be used by fraudsters to access your accounts at numerous financial institutions. I must add, I have never had any type of emotional disorder inside my life and am a skeptic of anti-depressants. You should find these details somewhere inside “Contact Us” section with the website.
Online health products
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can get a lot more done in a calm friendly manner then you definitely ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. Drugs could be ordered by simply entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click with the mouse button. Most drugs need to become stored at exact temperatures, so one in the things pharmacists learn as part of pharmaceutical quality training is the necessary steps to hold the facilities clean and in compliance with regulations.
Online pharmacy for pet medications
Remember the Golden Rule: As hard as it may be some times, you can get a lot more done inside a calm friendly manner then you certainly ever will accomplish by pounding your fist for the counter. ” A good response to this is just not “I’m seeking a job. Make sure that you take some time to ask about a more affordable version so they will look at the list.
Gabapentin online consultation
To get the most out with the card, put it to use every visit and keep track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. To find degree programs that train you to get a career as a pharmacy technician, you are able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. They also can check with doctors to authorize refills, and enter drug information in the computer.
Online pharmacy for diabetes medications
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing having a write-up that contained slightly of Schadenfreude. The pharmacist technician should have the prepared prescription, reviewed by way of a pharmacist, before dispensing or submitting the completed order to some patient or customer. If you receive prescriptions on a monthly basis make sure your pharmacy has your most up-to-date prescription insurance information.
Buy cholesterol medication online
It doesn’t seem fair people don’t have cheap drugs available to them for purchase and that they are burdened with spending most of their life worrying about a thing that could affect their survival like this. Drugs may be ordered by simply entering the pharmacy website and placing an order having a click from the mouse button. In order to register while using GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain the 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Online pharmacy loyalty program
It could be used by fraudsters to get into your accounts at a variety of financial institutions. Fear not, as time passes you will know exactly how to handle different varieties of problems that will come about. The application deadline is late April, but it’s best to apply much sooner.
Online pharmacy for asthma inhalers
To get the most out of the card, apply it every visit whilst track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. These will be the pharmacist who works being a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent of their time in the other areas of pharmacy. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we now have better chances of being successful.
Safe online pharmacy
While there is really a small chance you could get laid off (by way of example, in the event the chain supermarket closes some stores) you shouldn’t have much problem finding another job. The local temperature of the medicine producing country is one along with the other country might be another, along with the avian temperature is the other. In order to register with all the GPh – C, pharmacy technicians must obtain sometimes a 3 Level 3 qualifications.
Amoxicillin delivery service
Location and the form of employer would be the final factors in determining simply how much pharmacists make. Fear not, eventually you will know precisely how to handle different types of problems that will come about. The application deadline is in late April, but it’s best to apply much sooner.
Losartan mail-order pharmacy
The pharmaceutical industry especially cannot afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treatment of clients due on the perceived using any medical device, maybe it’s a pill or possibly a syringe. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( has used from the fraudster. There is basically no difference between ordering drugs from a drugstore within the United States than by having a Canada pharmacy except for that price.
Losartan mail-order pharmacy
It doesn’t seem fair people do not have cheap drugs open to them for purchase and that they’re burdened with spending the rest of their life worrying about something could affect their survival like this. ” A good reaction to this isn’t “I’m seeking a job. Make certain that you take the time to ask about a more affordable version so that they will check the list.
Online pharmacy for mental health
By giving your pharmacy the complete name of your respective medication it is possible to better safe guard your health. Insurance is confusing to start with, and it also is constantly changing. Strong customer support skills are a must when handling the hectic pace of your pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Online pharmacy safety tips
Pharmacy technicians also tend not to provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or another drug information. Ask the managers of the places in which you enjoy shopping if they have these forms of programs, should you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Online pharmacy for heart medications
“(3) The Washington Post(4) commemorated the closing which has a write-up that contained just a bit of Schadenfreude. Fear not, eventually you will know the best way to handle different kinds of problems that may come about. They are also to blame for inspecting the operational management of dispensary and manufacturing units and providing a platform to further improve the pharmacists’ role to prescribe medicine independently.
Sertraline discount pharmacy
There are two ways for being a pharmacist technician, getting certified or registered because of your state. To find degree programs that train you for a career as a pharmacy technician, you’ll be able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. However, by exercising with adequate practice pharmacy technician test questions we now have better odds of being successful.
Online pharmacy for travel medications
While there is often a small chance you have access to laid off (for example, when the chain supermarket closes some stores) you mustn’t have much problem finding another job. Drugs may be ordered just by entering the pharmacy website and placing an order using a click of the mouse button. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe will be the two names you should be looking out for as well as these names will proclaim why these websites feel safe for paying online.
Buy over-the-counter drugs online
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or becoming rude can’t help the situation. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists execute a lot over provide prescriptions to patients.
Online pharmacy for diabetes medications
To obtain the most out from the card, utilize it every visit and make track of coupon restrictions and expiration dates. These would be the pharmacist who works as being a professor or lecture in any medical college; they spend around 50 per cent with their time in the other areas of pharmacy. If possible try to use the identical pharmacy around possible.
Online pharmacy for pet medications
Most patients were paying a high income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or they’d not met their $4,000 deductable and must give the entire cost out-of-pocket. Screaming, yelling, demanding things, or just being rude can’t help the situation. Instead, I simply copied the url and pasted it into my browser window, and created exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Online pharmacy for diabetes medications
Also, look for the bargain table near the front with the store brimming with items as much as 50 percent from the regular price. The holding, the transfers, the modern rules and also the mail-order requirements. Use those outlines like a roadmap to help you you study to the pharmacy tech certification test.
Online pharmacy for skin treatments
The certification does play a crucial role in making a rewarding career as being a PT as it helps for making one more qualified after they apply for promotion. The above image shows that a secure protocol ( has used by the fraudster. If possible try to use the identical pharmacy around possible.
Buy antidepressants online
The pharmaceutical industry especially can’t afford to allow its practitioners to delay or refuse treating clients due on the perceived using any medical device, it could be a pill or perhaps a syringe. To find degree programs that train you for the career being a pharmacy technician, you are able to check out the Directory of Schools website at directoryofschools. So as a buyer, you will need to identify a traditional online pharmacy which is licensed and sells only Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved medicines.
Amoxicillin delivery service
If you happen to be disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you generally may have your student loans discharged. In 1960, the Ayala Group of Companies offered Mariano Que a place to lease inside shopping center that was about being developed inside the heart of Makati. According for the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), pharmacists do a lot more than provide prescriptions to patients.
Order anxiety medication online
1 teaspoon grated fresh ginger, or 1-2 lumps of preserved ginger, chopped. As a little entrepreneur, just when was it time to boost prices like Netflix. Instead, I simply copied the link and pasted it into my browser window, and came up with exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Gabapentin online consultation
Confira aqui a lista de hotéis recomendados No jogo Big Bass Splash, os jogadores embarcam em uma jornada emocionante em busca de prêmios substanciais. Com uma configuração padrão de 5 rolos, 3 linhas e 10 linhas de pagamento fixas, o jogo oferece uma experiência de jogo envolvente para jogadores de todos os níveis de habilidade. O objetivo é simples: formar combinações vencedoras de símbolos nos rolos para garantir prêmios incríveis. Dia 23 07 – 10:00 às 20:00 Para desfrutar do Big Bass Splash, os jogadores precisam se registrar em um cassino online que ofereça o jogo. Após o registro e o depósito, os jogadores podem localizar o jogo no cassino e ajustar o valor da aposta de acordo com suas preferências, com apostas que variam entre R$ 0,50 e R$ 1.250. You can email the site owner to let them know you were blocked. Please include what you were doing when this page came up and the Cloudflare Ray ID found at the bottom of this page.
https://klcmarketingsales.com/2025/07/13/aviatrix-casino-game-review-and-download-guide-for-android-ios-players-in-india/
SLOTS | FISHING | HIGH VOLATILITY | 4WIN O Big Bass Splash é um slot que pode ser comparado a outros jogos de cassino online por sua simplicidade e dinâmica, lembrando que, em geral, os slots diferem de jogos que exigem mais estratégia, como Poker ou Blackjack, já que dependem do acaso. Os principais cassinos com rodadas grátis de 2025 são a Novibet, F12.Bet, KTO, Luva.bet e Estrelabet. Informamos aos passageiros que a linha semi-direto Florida – POA via Praia de Belas, no sentido ida, terá o itinerário via Túnel da Conceição a partir de segunda-feira dia 10 02 2025. Também é importante entender que nem todo cassino online oferece apostas de 10 centavos para slots. Isso vai depender da provedora e da operadora. No cassino da KTO, você encontra uma ampla seleção de slots com apostas a partir de 10 centavos, incluindo o Big Bass Bonanza e outros títulos da série Big Bass.
Pharmacy technicians also don’t provide advice to patients about medication options, unwanted side effects, or another drug information. In Oklahoma, pharmacists are forced to obtain a valid photo identification before dispensing any controlled, dangerous substance. Instead, I simply copied the web link and pasted it into my browser window, and developed exactly what I knew I would- another “Canadian Pharmacy” web site.
Online pharmacy loyalty program
By giving your pharmacy the complete name of one’s medication you can better safe guard your health. Before taking any exams necessary for their state, they need to pass the Foreign Pharmacy Graduate Equivalency examination (FPGEE), Test of English being a Foreign Language (TOEFL) and Test of Spoken English (TSE) exams. Strong customer care skills can be a must when handling the hectic pace of an pharmacy or pharmaceutical department.
Online pharmacy for contraceptives
If you are disabled as outlined by federal government standards, and receive government disability payments, then you generally may have your student loans discharged. Ask the managers with the places where you enjoy shopping if they offer these varieties of programs, in case you aren’t already frequenting CVS and Winn-Dixie. com or call 877 636 Rx – Rx – About The Founders – Sandy A Reese Rigg, RN, Rph – Susan Chin Jackson, RPh – Both graduated from St.
Safe online pharmacy
Most patients were paying a high income for their insurance and were often upset when their prescriptions required a $50 co-pay, or that they had not met their $4,000 deductable and must pay for the entire cost out-of-pocket. As a little entrepreneur, just when was it time to boost prices like Netflix. The respiratory therapist’s tasks include offering the precise measurements of oxygen or other types of gas concentrations inside the patient’s blood along with measuring blood alkalinity or acidity levels.
Prescription allergy medications online
CVS Pharmacy must rely on prescription drug sales to be in business, but Wal-Mart doesn’t ought to add a huge markup to the prescription medications they sell. When all factors are believed, however, I would have to say how the prices charged at CVS Pharmacy and Rite Aid Pharmacy may be comparable. Veri – Sign and Scan – Alert Hacker Safe are the two names you need to be looking out for as well because they names will proclaim these websites are safe for paying online.
Gabapentin online consultation
It’s awesome to pay a visit this site and reading the views of
all colleagues concerning this piece of writing,
while I am also keen of getting knowledge. https://tinyurl.com/2c2rno87 what is vpn stand for
I blog quite often and I really appreciate your content.
The article has really peaked my interest. I’m going to book mark
your site and keep checking for new details about once
per week. I opted in for your Feed too.
I’m no longer sure where you’re getting your information, but good topic.
I must spend some time finding out more or understanding more.
Thanks for great information I was looking for this information for my mission.
I’ll immediately snatch your rss as I can not find your email subscription hyperlink
or newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me realize so
that I could subscribe. Thanks. Eharmony special coupon code
2025 https://tinyurl.com/ylp5rfgb
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
J881love, never heard of it before. Let’s dive in and see if the games live up to the name! Hoping for a good selection and some awesome promotions. Let’s see what it offers: j881love
811bet7, huh? Gave it a spin last night. Solid platform, decent odds. Nothing earth-shattering, but reliable. Here’s the link: 811bet7
If you’re looking for an apk to bet with rupees, Betrupeesapk is the way to go. Seems pretty legit, and I haven’t had any issues so far. Happy betting! betrupeesapk
Superwincasino, here I come! Hoping for a super win. Ready to test my luck and have some fun! Fingers crossed! Let’s enjoy at superwincasino!
I really like it whenever people get together and share views.
Great blog, keep it up! vpn https://www.highlandguides.com
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Signed up for bonos777club because of the perks. I have to say its worth a peek. You’ll find awesome content: bonos777club
Heard about 666betfreebet offering some free bet action, and I had to try it out. The promo was pretty sweet, easy to claim, and I actually managed to win a little something! Website design isn’t ground-breaking, but it works. See what freebies you can get over at 666betfreebet.
Getting into KG777 was quick and painless with kg777login. No weird hoops to jump through, just smooth sailing. The games inside are legit, and there’s a good mix of stuff. Check out kg777login if you’re looking to sign up.
Tried c77game the other day. I was pleasantly surprised by the variety. Graphics were pretty good too. It’s worth a look if you’re bored of the same old casinos. Head over to c77game and see what you think!
Gamebet6 is aight, got some cool games I haven’t seen anywhere else. Not the flashiest site, but it gets the job done. Worth a peek, for sure! Here’s the link: gamebet6
Undeniably believe that which you said. Your favorite justification appeared to be on the internet the easiest thing
to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while people consider worries that
they plainly don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole
thing without having side effect , people can take a signal.
Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
Visit My website – Great explanation! I’ve been searching for this info for days.
Nice post. I was checking continuously this blog and I’m impressed!
Extremely helpful information specifically the last part 🙂 I care for such information a lot.
I was looking for this certain information for a very long time.
Thank you and best of luck.
Unquestionably believe that which you said. Your favorite justification seemed to be
on the web the simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you,
I definitely get annoyed while people think about worries that they plainly don’t know about.
You managed to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing without having side-effects ,
people can take a signal. Will probably be back to get more.
Thanks
My spouse and I stumbled over here different website and thought I might check
things out. I like what I see so now i am following
you. Look forward to looking into your web page yet
again.
Hello there! I know this is kind of off topic but I was wondering if
you knew where I could find a captcha plugin for my comment form?
I’m using the same blog platform as yours and I’m having difficulty finding one?
Thanks a lot!
Wow, this piece of writing is pleasant, my younger sister is analyzing these kinds of
things, so I am going to convey her.
Bingo Patti, that’s my jam! I love bingopattigame. Super fun and colorful. Can totally lose track of time playing. Try it if you’re into that sort of thing: bingopattigame
Honestly, Xpgamesbet surprised me. Usually skeptical of these things, but they have got me hooked. Cool games, easy to use too: xpgamesbet
If you need the 1xbet app, 1xbetdownloadapk is where I got it. Easy download, no problems installing. Gets you betting on the go real quick. Get it here 1xbetdownloadapk.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
In fact when someone doesn’t be aware of afterward its up to other visitors that they will help, so here it takes place.
**balmorex pro**
balmorex is an exceptional solution for individuals who suffer from chronic joint pain and muscle aches.
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.